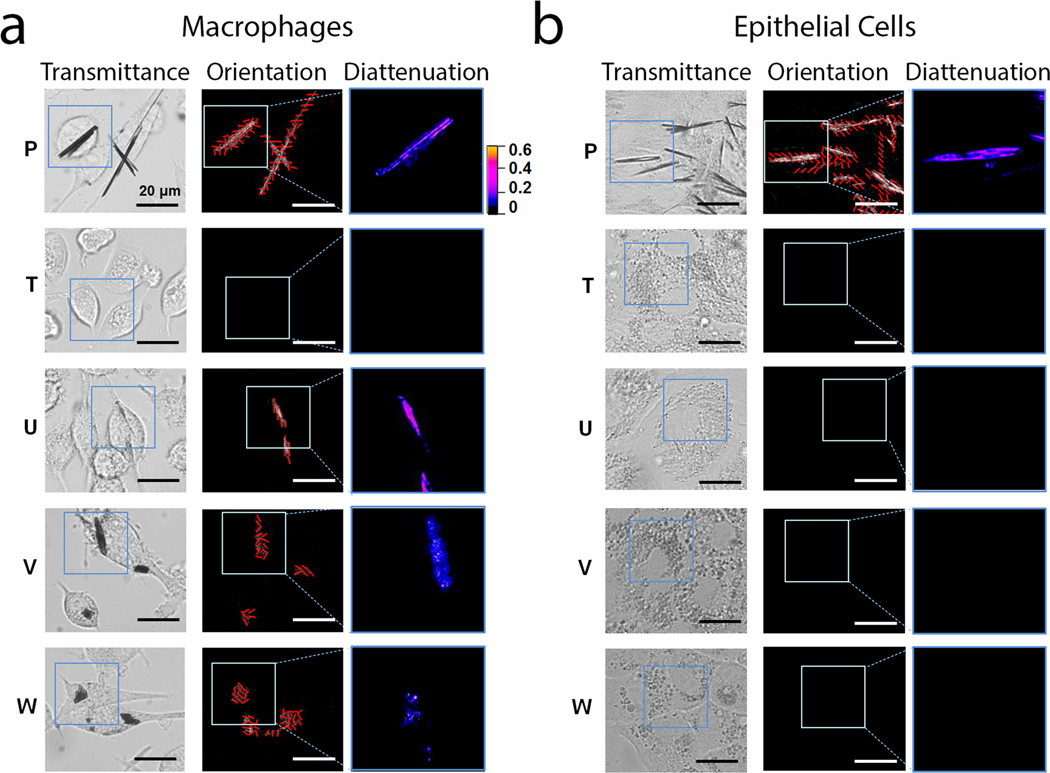
Figure 3.
Quantitative polarization microscopy of macrophages and epithelial cells incubated with the different phenazine compounds revealed cell type-specific differences in transmittance, diattenuation anisotropy, and the orientation of the polarization axis maximal transmittance of the intracellular inclusions. For the experiments, live RAW264.7 macrophages (a) or MDCK epithelial cells (b) were incubated for 72 hours with clofazimine or other phenazine analogs, and analyzed with the diattenuation anisotropy microscope imaging set up, using monochromatic light of 546 nm wavelength. Transmittance corresponds to the image map of the transmitted light intensity at 546 nm wavelength (white corresponds to 100% transmittance and black corresponds to 0% transmittance); Orientation corresponds to the measured direction of maximal light transmittance of linearly polarized light across the sample, indicated with a grid of red lines superimposed on the image. Diattenuation corresponds to the quantitative diattenuation anisotropy image map measured using linearly polarized light of 546 nm wavelength. The color-gradient calibration bar corresponds to diattenuation anisotropy values ranging from 0 to 0.6. Scale bar = 20 µm.