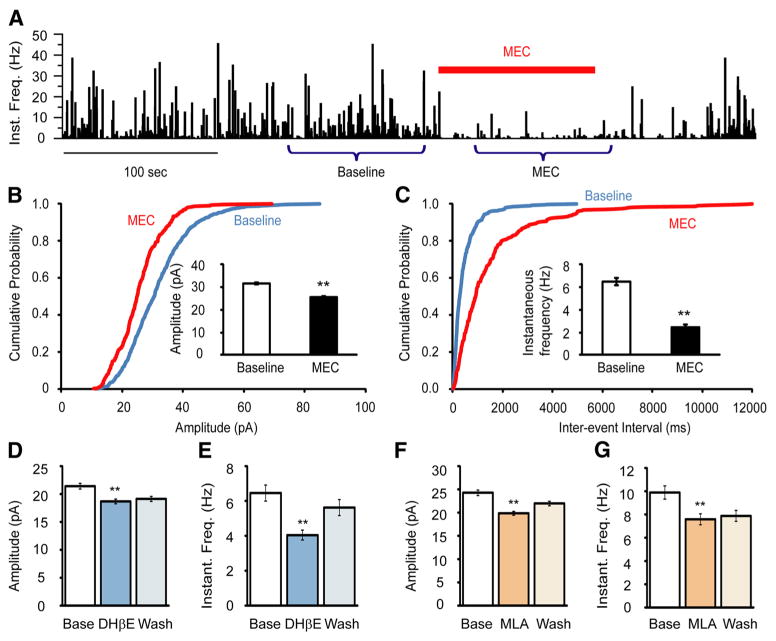
Figure 6.
Nicotinic AChR antagonists suppressed glutamatergic mEPSCs onto Hcrt+ neurons. A, Mecamylamine, a nonselective nAChR antagonist, strongly suppressed mEPSCs onto Hcrt+ neurons. The bar above the graph indicates the duration of MEC (10 μM) exposure. Miniature EPSCs from two periods of time (Baseline and MEC) were used for analysis. B, Cumulative probability plot of the mEPSC amplitude at baseline and during MEC exposure was made from the recordings of four cells. Inset shows the mean values of the mEPSC amplitude at baseline and following MEC exposure. **p < 0.01. C, Interevent intervals of mEPSCs at baseline and upon MEC application from four cells (same cells as in C). Inset shows the mean instantaneous frequency of the mEPSCs at baseline and following MEC exposure. D, E, DHβE, an antagonist of heteromeric nAChRs (particularly α4β2 nAChRs), moderately suppressed the amplitude (D) and instantaneous frequency (E) of mEPSCs onto Hcrt+ neurons. n = 7 cells. F, G, MLA, a relatively selective α7 nAChR antagonist, partially suppressed mEPSC amplitude (F) and instantaneous frequency (G). n = 8 cells.