Figure 3. Crystal structure of the RTO-Fab/PF4 monomer complex.
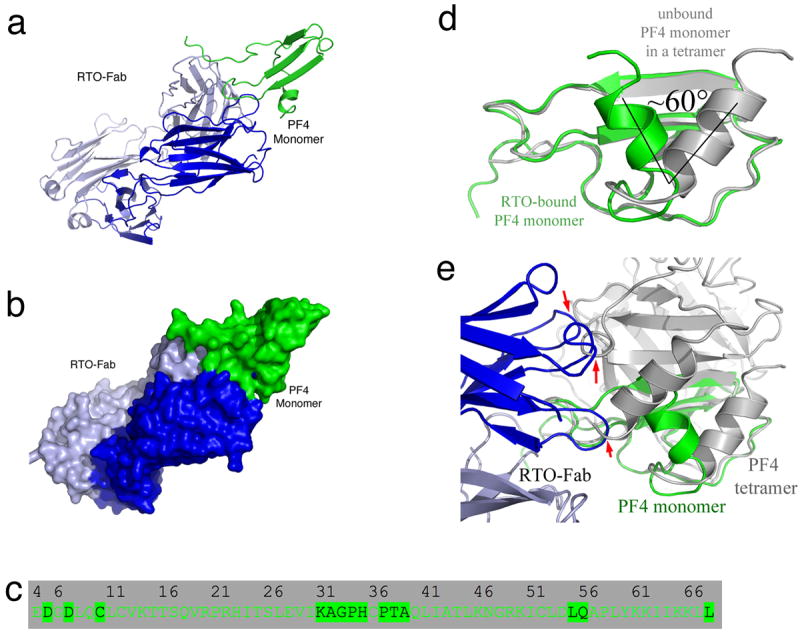
(a,b) Overall structure of the PF4/RTO-Fab complex. a: cartoon representations of the complex; b: molecular surface representations. The heavy chain and light chain of RTO-Fab are colored in blue and light blue, respectively. (c) Detailed binding interface of the non-HIT antibody RTO to a PF4 monomer. Residues of a PF4 monomer that are less than 5 Å away from RTO-Fab molecule are highlighted. (d) Superposition of the PF4 monomer (green) in the RTO-Fab/PF4 complex with that in the unbound PF4 (gray) indicates that binding of RTO-Fab causes a dramatic structural change in the PF4 monomer: the C-terminal helices are shifted ~60°. (e) Superposition of the PF4 monomer (green) in complex with RTO-Fab (blue and light blue) with the unbound PF4 tetramer (gray). The three arrows indicate the sites where binding of RTOFab to one PF4 monomer causes steric clashes with a second PF4 monomer in the tetramer, thereby preventing tetramer formation.
