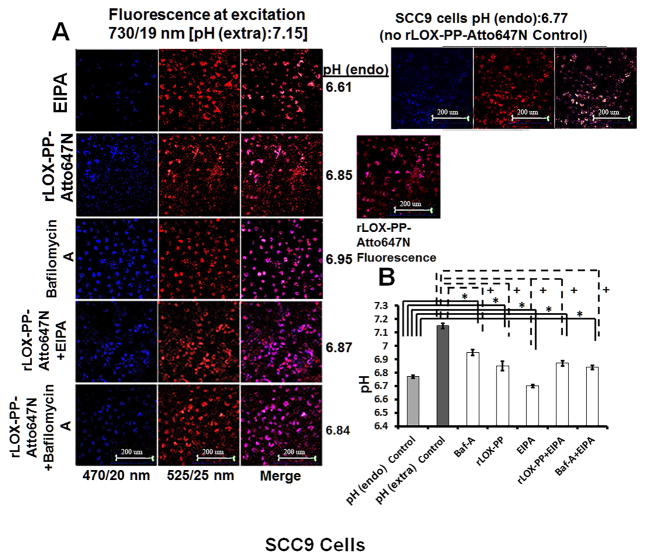
Figure 12. Internalized rLOXPP-Atto647N increased endosomal pH from 6.77 to 6.85.
In (A), SCC9 cells were maintained in the recording buffer at pH 7.15 for steady state extracellular pH and incubated with Lysosensor Yellow/Blue dextran +/− rLOX-PP-Atto647 and/or EIPA or bafilomycin A for 3 hours. Images were obtained by confocal microscopy with a 20x objective and Lysosensor Yellow/Blue dextran emission was collected in 470 +/− 20, 490 +/−10 and 525 +/− 25 nm band ranges. 470 +/− 20 and 525 +/− 25 nm were artificially colored as blue and red consecutively. 470 +/− 20 (blue) and 525 +/− 25 (red) emission ratios were compared with the calibration curve. 675 nm and higher rLOX-PP-Atto647N emission was collected and artificially colored as magenta. (Artificially magenta colored emission integral of rLOX-PP-Atto647N was collected to avoid overlap between Yellow/Blue dextran 10,000 and rLOX-PP-Atto647N emission in rLOX-PP-Atto647N treated samples). In rLOX-PP-Atto647N treated cells, the merged image on the right side shows that rLOX-PP-Atto647N and Lysosensor Yellow/Blue dextran 10,000 MW co-localize. Images show endosomal pH (pH endo) measurements which change as a function of either rLOX-PP-Atto647N bafilomycin A1, EIPA and combinations in SCC9 cells ((images were collected with EC-Plan Neofluar 40x/1.30 oil DIC M27 objective). The excitation wavelength was 740 nm (two photon), and emission was detected in 4 channels: 470/20, 490/10 and 525/25 nm for Lysosensor Yellow/Blue dextran 10,000 MW, and 669/25 nm for rLOX-PP-Atto647N.
In (B), SCC9 cells were treated with either both rLOX-PP-Atto647N and EIPA or bafilomycin A1 and EIPA to assess whether rLOX-PP-Atto647N or bafilomycin A1 can reverse the endosomal pH drop caused by EIPA treatment.