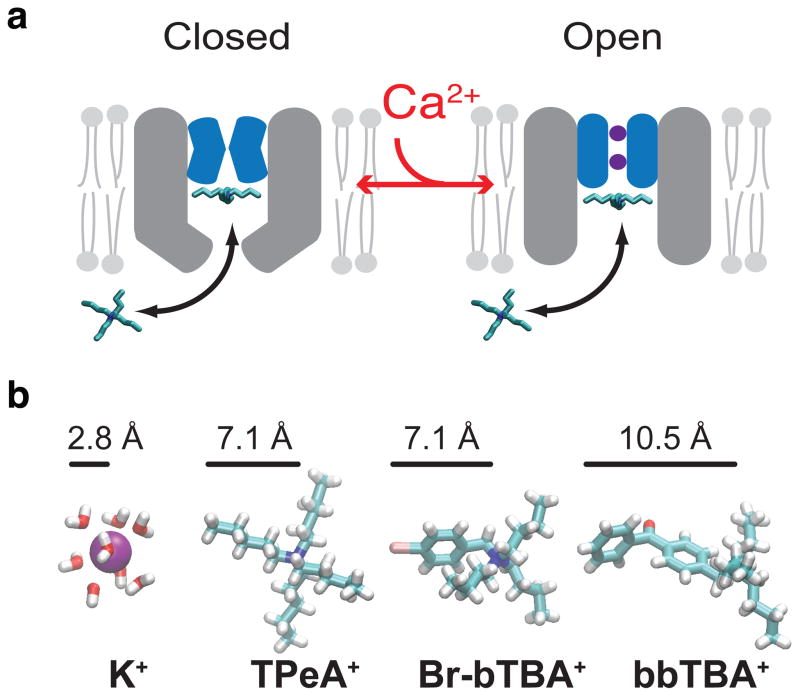
Figure 5. Closure at the MthK selectivity filter is accompanied by a conformational change near the intracellular entryway.
(a) Model for QA block of the closed and open MthK channel. The selectivity filter is non-conductive in the absence of Ca2+ and the intracellular entryway (grey) is narrowed but still allows blocker/K+ entry into vestibule (left). Channel activation opens the selectivity filter gate (purple K+ inside blue filter) and increases blocker access rate into the pore (right). (b) The radius of a hydrated K+ is smaller than the extended structures in TPeA+, Br-bTBA+ and bbTBA+, suggesting that K+ can access the closed MthK intracellular entryway despite the constriction.