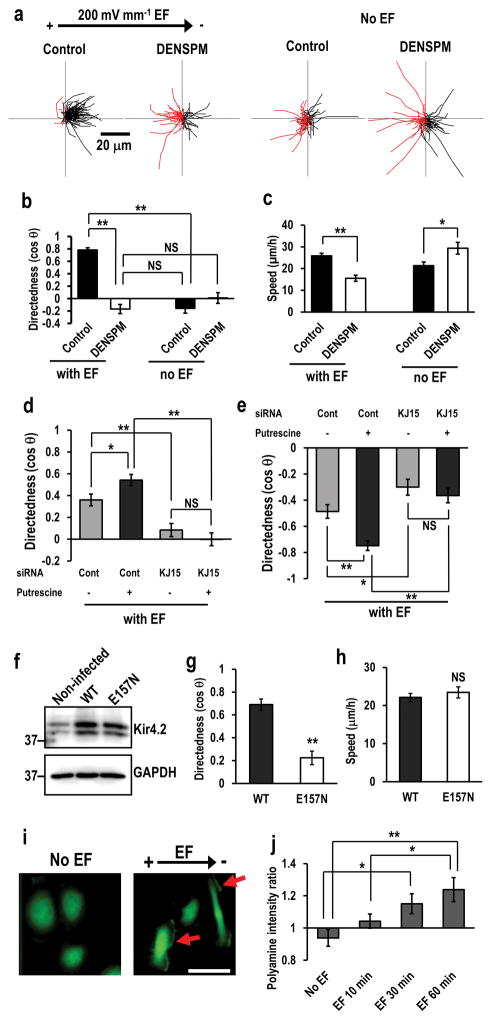
Figure 5. KCNJ15 couples with polyamines to sense extracellular EFs.
(a, b) Intracellular polyamines are required for cells to sense extracellular EFs. Depletion of polyamines with DENSPM abolished galvanotaxis. Migration trajectories of control cells and DENSPM treated cells with or without EF. Red lines indicate trajectories of cells migrated toward anode side. hTCEpi cells were treated with 25 μM DENSPM for 2 days. DENSPM activates spermine/spermidine catabolizing enzyme SAT/SSAT which catabolizes spermine/spermidine to N1-acetyl spermine/spermidine and reduces intracellular polyamine.
(c) Depletion of polyamines affected cell migration speed.
(d, e) Increased intracellular polyamines significantly enhanced galvanotaxis of U251 cells (d), or HaCaT cells (e). Knockdown of KCNJ15 canceled putrescine-enhanced galvanotaxis. Cells were transfected with control oligo or KCNJ15 siRNA, and treated with or without putrescine (100 μM) for 2 days.
(f) Lentivirus-mediated expression of wild-type and E157N Kir4.2 proteins. hTCEpi cells transduced with lentivirus. The Expression of wild-type (WT) and polyamine-binding defective mutant (E157N) Kir4.2 proteins was confirmed by Western blotting.
(g, h) Expression of polyamine-binding defective mutant of KCNJ15 (E157N) significantly decreased directedness but had little effect on cell motility. hTCEpi cells were infected with recombinant lentivirus and incubated for 2 days. Directedness and speed were evaluated.
(i, j) An applied EF-induced asymmetry of intracellular polyamines. Representative image of the polyamine staining (i). Scale bar in (i), 50 μm. Intensities of polyamines staining in cathode facing side were divided by those in anode facing side (right side divided by left side in no EF cells) (j), Polyamine distribution in response to EF. hTCEpi cells were subjected to EF (200 mV mm−1) for 0, 10, 30 or 60 min. Intracellular polyamines were stained with anti-polyamine antibody. Arrows in (i) indicate polyamine accumulation in cathode facing side of hTCEpi cells.
Statistics: b and c: n=100 cells for each group, confirmed in 3 independent experiments. d: n=50, e: n=120, g and h: n=120, j: n=16–23, All confirmed in 2–3 separate experiments. EF =200 mV mm−1. Statistical analyses were performed by Student’s t-test (b, c, d, e, g and h), or ANOVA followed by the Student’s t-test (j). Data represented as mean ± SEM. *, p<0.05. **, p<0.01. NS, no significance.