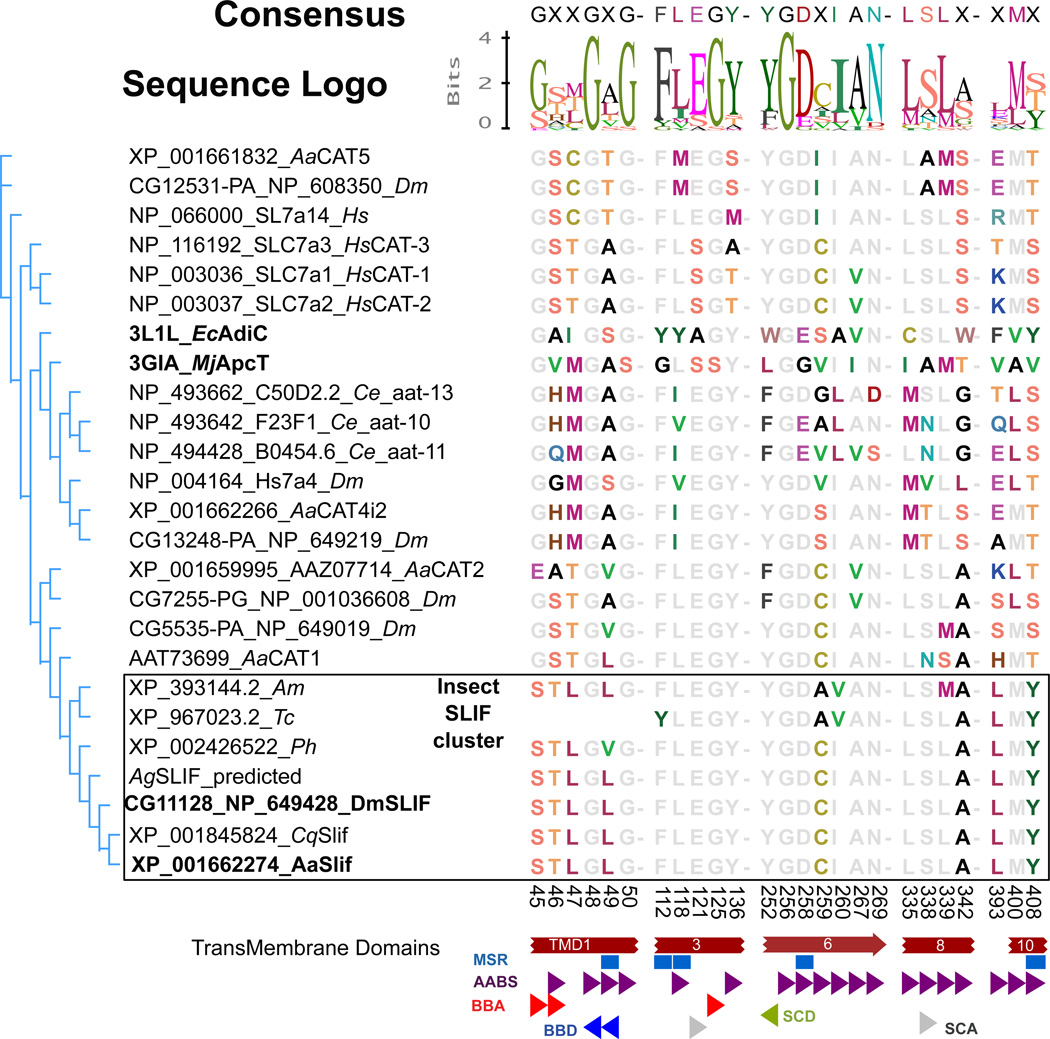
Fig 1. Bioinformatics analysis of the AaSlif SBM.
Shown are a Neighbor-Joining consensus tree and an alignment of the putative Substrate Binding Motif (SBM) residues of selected CAT-SLC7 members. Putative Slif orthologs (outlined box) form phylogenetic cluster with exactly one ortholog per selected insect genome and also show strong conservation of the SBM. The names of Drosophila and Aedes slif orthologs and their prokaryotic homologs used for the identification and alignment of SBMs are highlighted by bold font. Colored and gray fonts depict variable and significantly conserved residues, respectively. The aligned numbers indicate the amino acid positions in the AaSlif protein sequence. The partial SBM of the Tribolium Slif is due to its incomplete annotation. The colored shapes depict specific putative component of the SBMs abbreviated as: AABS, amino acid binding sites; BBA, backbone acceptor; BBD, backbone donor; MSR, mutation sensitive residues; SCA, side chain acceptor; SCD, side chain donor. Species abbreviations are: Aa, Aedes aegypti; Ce, Caenorhabditis elegans; Cq, Culex quinquefasciatus; Hs, Homo sapiens, Ph, Pediculus humanus, Tc, Tribolium castaneum.