Figure 1.
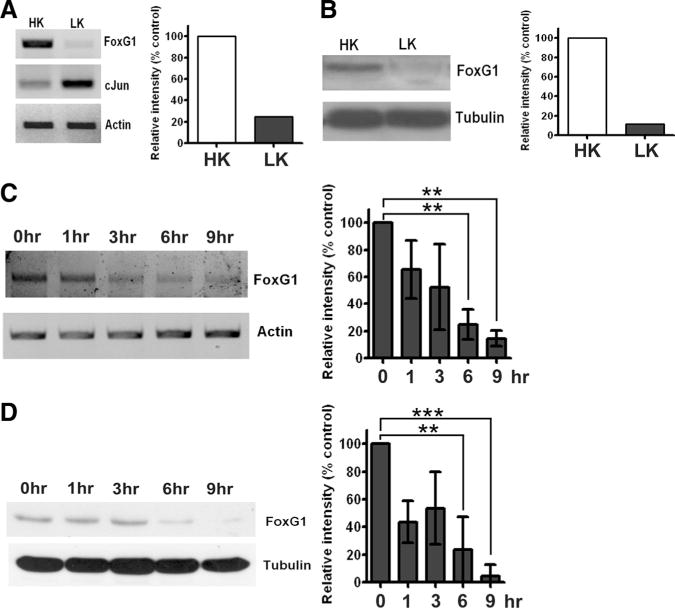
Expression of FoxG1 in postmitotic neurons. A, RNA isolated from CGNs treated with HK or LK for 6 h were subjected to RT-PCR analysis of FoxG1 expression. FoxG1 mRNA expression is reduced at 6 h of LK treatment. Incontrast, the expression of the proapoptotic c-Jun gene is induced in neurons primed to die by LK treatment. Actin serves as the loading control. B, Whole-cell lysates were prepared from CGNs treated with HK or LK for 6 hand subjected to Western blot analysis using a FoxG1 antibody. FoxG1 is downregulated in LK. Tubulin serves as the loading control. C, RNA isolated from CGNs treated with LK for 0, 1, 3, 6, and 9 h was subjected to RT-PCR analysis of FoxG1 expression. Actin served as loading control. Densitometric analysis indicates reduction of FoxG1 mRNA level with time. Results were obtained from three separate experiments. **p < 0.01. For statistical analysis, one-way ANOVA was performed using Bonferroni’s multiple-comparisontest. D, Whole-cell lysates prepared from CGNs treated with LK for 0, 1, 3, 6, and 9 h were subjected to Western blot analysis using a FoxG1 antibody. Tubulin serves as the loading control. Densitometric analysis indicated reduction of FoxG1 protein level with time. Results were obtained from three separate experiments. ***p< 0.001, **p< 0.01. For statistical analysis, one-way ANOVA was performed using Bonferroni’s multiple-comparison test.
