Figure 2.
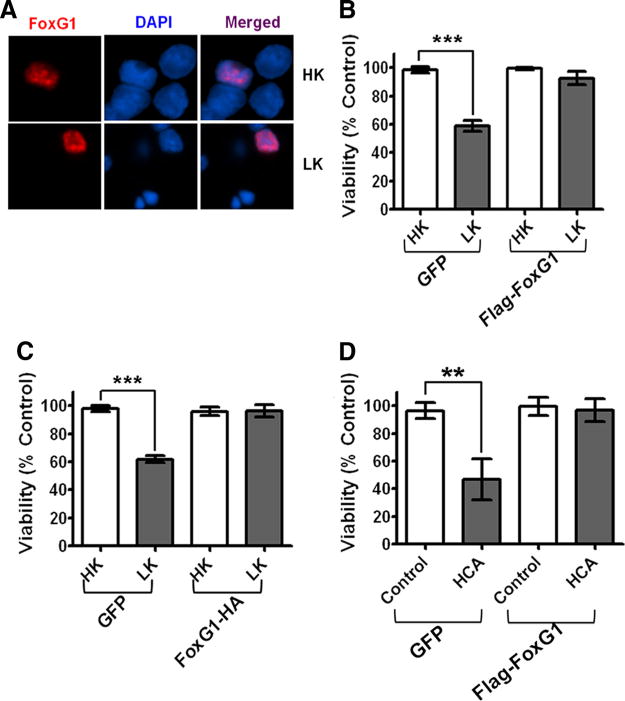
Effect of FoxG1 overexpression in postmitotic neuronal survival: CGN cultures were transfected with GFP and Flag-FoxG1 or FoxG1-HA for 12 h and then switched to HK or LK medium for 24 h followed by immunocytochemistry. The viability of transfected neurons was quantified by DAPI staining and normalized to GFP-transfected cells in HK. FoxG1 protects neurons independent of its tag. A, Localization of ectopically expressed FoxG1 in CGNs. Transfected neurons were identified by immunocytochemistry using Flag antibody. FoxG1 localizes exclusively in the nucleus in HK- and LK-treated neurons. B, FoxG1 protects CGNs from LK-induced apoptosis. C, CGN cultures transfected with either GFP or FoxG1-HA. FoxG1-HA protects neurons from LK-induced apoptosis. Results were obtained from three separate experiments done in duplicate. ***p< 0.001 as compared to control (GFP-transfected neurons in HK). D, Two-day-old cultures of primary cortical neurons transfected with GFP or Flag FoxG1 were treated with either medium having no additives (NA) or medium containing 1 mM HCA for 20 h. Viability of transfected neurons was quantified after immunocytochemistry using GFP or Flag antibody and normalized to the viability of control cultures (GFP-transfected cells receiving no additives). **p< 0.01 as compared to GFP-transfected cortical neurons with NA.
