Figure 8.
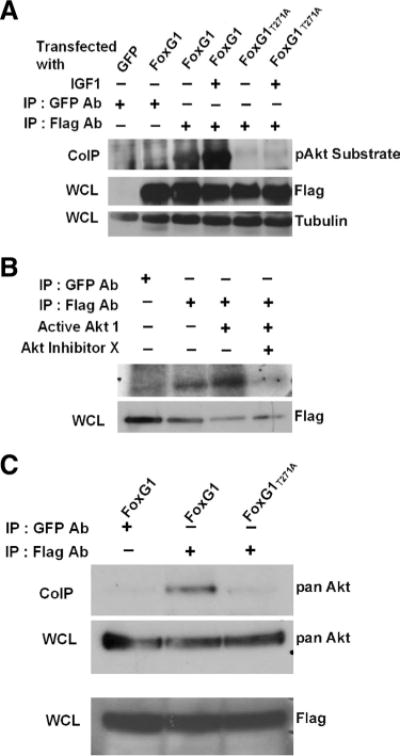
FoxG1 is a substrate of Akt. A, HEK293T cells were transfected with Flag-FoxG1 or Flag-FoxG1T271A and then treated for 15 min with IGF-1. Then FoxG1 was immunoprecipitated from the cultures using a Flag antibody, and the immunoprecipitate was subjected to Western blotting using a phospho-Akt substrate antibody. Lysates from GFP and Flag-FoxG1-transfected cells immunoprecipitated with a GFP antibody served as negative controls. Preimmunoprecipitation aliquots of the whole-cell lysates (WCLs) were subjected to Western blotting using Flag and Tubulin antibody to verify that similar amounts of lysates were used in each lane. Wild-type FoxG1 is phosphorylated in serum-containing medium not supplemented with IGF-1. The extent of phosphorylation is higher after exposure to IGF-1. FoxG1T271A is not phosphorylated even in the presence of IGF-1. B, Lysates from HEK293T cells transfected with Flag-FoxG1 were immunoprecipitated with antibodies to Flag or GFP (negative control) as indicated in the figure. The immunoprecipitate was used in an in vitro kinase assay performed in the presence or absence of active Akt enzyme. In one sample, a chemical inhibitor of Akt, Akt-X, was added to the kinase reaction mixture 15 min before addition of active Akt. Preimmunoprecipitation WCL was analyzed by Western blotting using a Flag antibody to verify that similar levels of FoxG1 were produced by transfection. C, HEK293T cells were transfected with Flag-FoxG1 or Flag-FoxG1T271A and pulled down with Flag or GFP antibody as indicated in the figure. Western blot analysis was performed with an Akt antibody. Flag-FoxG1 interacts with endogenous Akt, whereas Flag-FoxG1T271A fails to do so. Preimmunoprecipitation WCLs were analyzed by Western blotting using a Flag antibody to verify that similar levels of wild-type and mutant FoxG1 were produced by transfection.
