Figure 2.
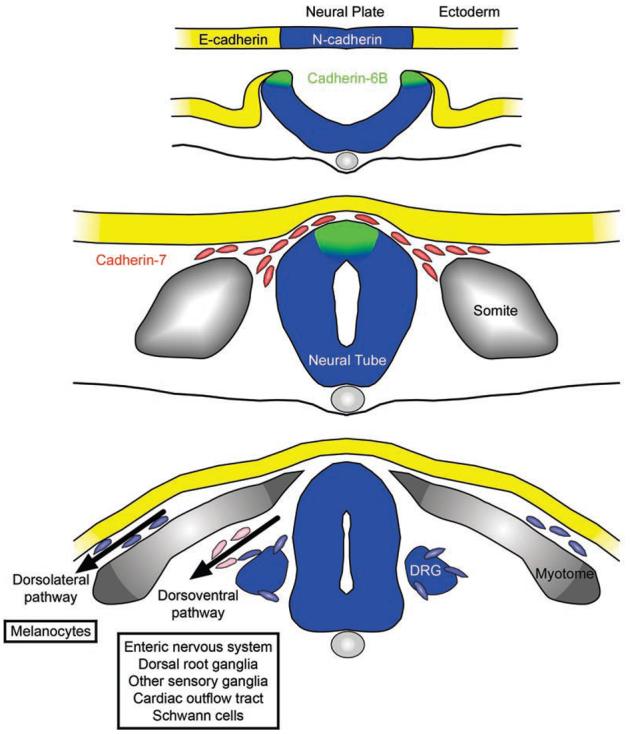
Cadherin expression during the formation of the neural crest in the avian embryo. Prior to neurulation, E-cadherin (yellow) is expressed throughout the developing embryonic ectoderm. The neural plate is later defined by the acquisition of N-cadherin (blue) and the loss of E-cadherin, which is still maintained in the non-neural ectoderm or future epidermis. During neurulation, N-cadherin expression persists in the invaginating neural plate, while cadherin-6B (green) comes on in the neural folds of the embryo, delineating the future premigratory neural crest cell domain in the dorsal neural tube. Cadherin-6B and N-cadherin are downregulated as neural crest cells undergo EMT, and migratory neural crest cells instead express cadherin-7 (red) as they migrate along stereotypical pathways to their final destinations. During neural crest cell differentiation, N-cadherin expression is detected in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG). Pink cells along the dorsolateral pathway in the bottom panel of the figure indicate migratory neural crest cells expressing multiple cadherins. Structural derivatives of the dorsolateral and dorsoventral pathways are indicated in boxes.
