Figure 2.
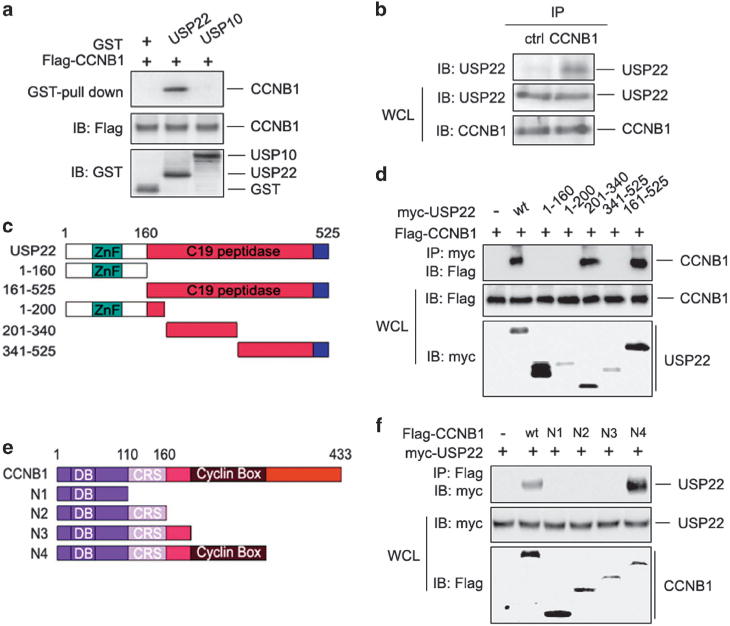
USP22 interacts with CCNB1. (a) HCT116 cells were transfected with Flag-tagged CCNB1 expression plasmid. After 48 h, cells were lysed and incubated with GST-USP22 or GST-USP10 and GSH-Sepharose as well. Proteins retained on Sepharose were then blotted with the indicated antibodies. (b) HCT116 cells were lysed, and the interaction between endogenous CCNB1 and USP22 was determined by immunoprecipitation of CCNB1 using normal rabbit IgG as control and immunoblotting with anti-USP22 antibody (top panel). (c) Domain structures of USP22 and its truncated mutants. USP22 contains an N-terminal zinc-finger domain and a C-terminal C19 peptidase catalytic domain. (d) CCNB1 expression plasmids were co-transfected with USP22 or each of the truncated mutants shown in c into HCT116 cells. The interaction between USP22 or its mutants and CCNB1 was examined. (e) Domain structures of CCNB1 and its truncated mutants. CCNB1 contains an N-terminal destruction box (DB), followed by a cytoplasmic retention sequence (CRS) and a cyclin box domain. (f) Myc-USP22 expression plasmids were co-transfected with CCNB1 or each of the truncated mutants shown in e into HCT116 cells. The interaction of CCNB1 or its mutants was examined. CCNB1, cyclin B1; IgG, immunoglobulin G; USP2, ubiquitin-specific protease 22.
