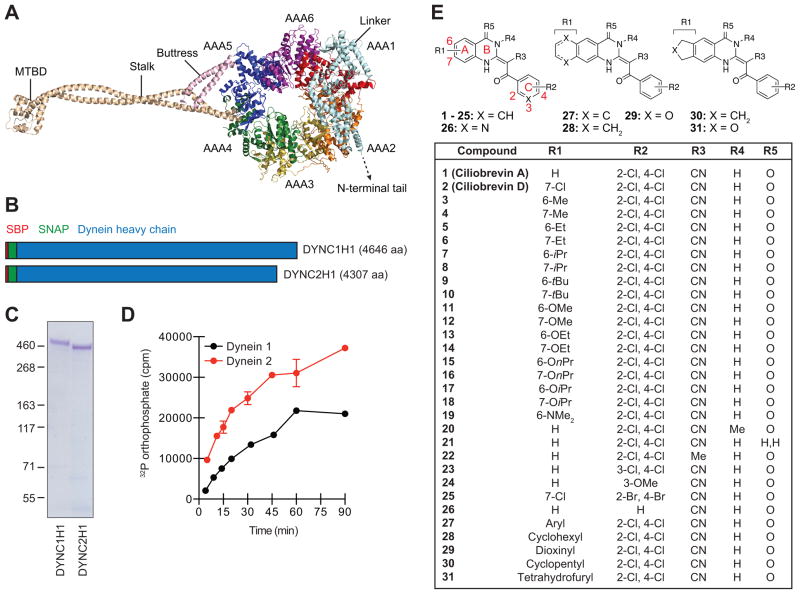
Figure 1. Cytoplasmic dynein heavy chains and ciliobrevin analogs used for structure-activity profiling.
(A) Cartoon representation of the dynein 2 heavy chain based on crystallographic data for the pre-power stroke conformation (PDB ID: 4RH7). Individual AAA domains within the C-terminal motor are shown, as well as the N-terminal linker, stalk, buttress, and MTBD. (B) Schematic representation of N-terminally SBP- and SNAP-tagged dynein heavy chains. Polypeptide domain lengths are shown to scale. (C) Purified SBP-SNAP-DYNC1H1 and SBP-SNAP-DYNC2H1 proteins resolved by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie Blue. (D) Kinetic analyses of dynein heavy chain activities, as determined by the hydrolysis of γ-32P ATP (17 nM) at 37 °C. Data are the average of two replicates ± s.e.m., and the enzyme reaction curves were used to establish linear assay conditions for the evaluation of ciliobrevin analogs. (E) Structures for the initial set of diverse ciliobrevin analogs profiled in this study.