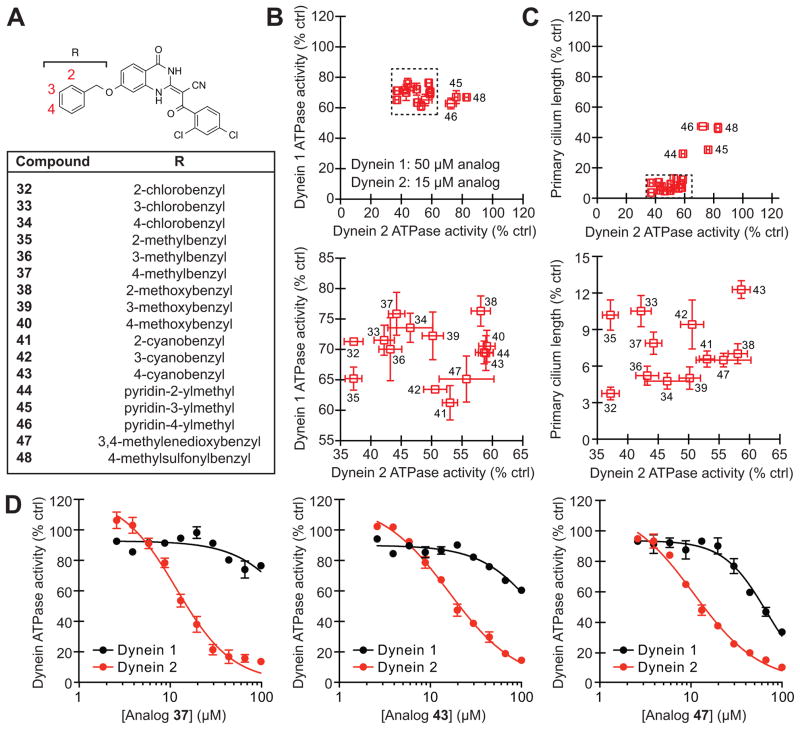
Figure 3. Benzyl ether-functionalized ciliobrevins with improved cytoplasmic dynein 2 selectivity.
(A) Structures for the focused library of ciliobrevin analogs. (B) Inhibitory activities of the C7-benzyl ether analogs in DYNC1H1 and DYNC2H1 ATPase assays. The compounds were tested in the presence of approximately 25 nM γ-32P ATP, and a lower inhibitor concentration was used in the DYNC2H1 assays since C7-functionalized analogs are generally more potent against this isoform. Data are the average of two experiments ± s.e.m. Tightly clustered analogs (dashed box) are re-plotted in the adjacent graph. (C) Correlation of analog activities in dynein heavy chain ATPase and ciliogenesis assays as described in Figure 2F. Tightly clustered analogs (dashed box) are re-plotted in the adjacent graph. (D) Dose-dependent inhibition of DYNC1H1 (black) and DYNC2H1 (red) ATPase activities by analogs 37, 43, and 47. Data are the average of triplicate samples ± s.e.m. Calculated IC50 values: 37, DYNC1H1 = 280 μM and DYNC2H1 = 11 μM; 43, DYNC1H1 = 158 μM and DYNC2H1 = 16 μM; 47, DYNC1H1 = 130 μM and DYNC2H1 = 11 μM.