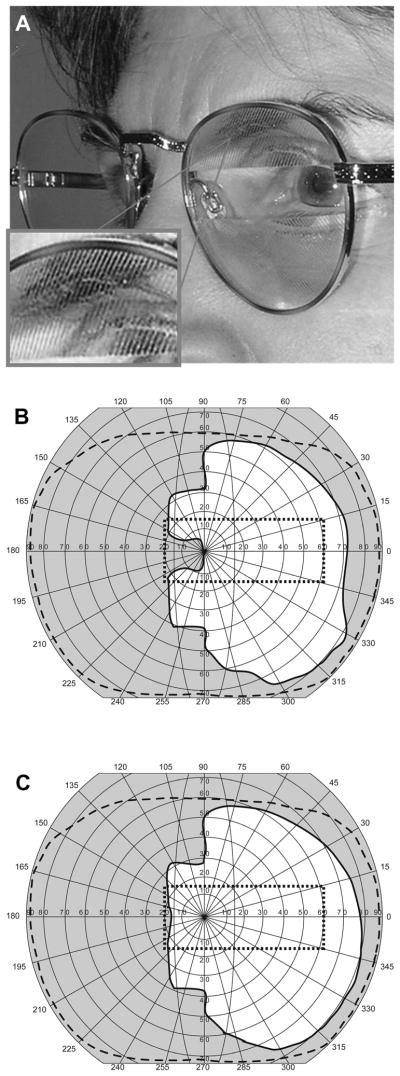
FIGURE 2.
(A) Peripheral prism glasses in the oblique design constructed with press-on Fresnel prisms of 40Δ (see magnified inset) above and below the pupil mounted on the back of the left lens only for a patient with left hemianopia. The upper segment is oriented with the base out and down and the lower segment with the base out and up. (B) Binocular visual field of a patient with left hemianopia with oblique press-on Fresnel 40Δ prisms with the apex-base axes at 30 degrees tilt and with 11-mm interprism separation. The vertical gap between the expansion areas is reduced compared with the horizontal design (Fig. 1C), but the lateral field expansion effect is a little smaller. Note that the field in Fig. 1C was measured with 36Δ prisms. (C) Binocular visual field of the same patient with the same prisms but with a separation of 9 mm, which further reduces the gap. The dotted rectangle indicates the field of view through the windshield of a typical car.