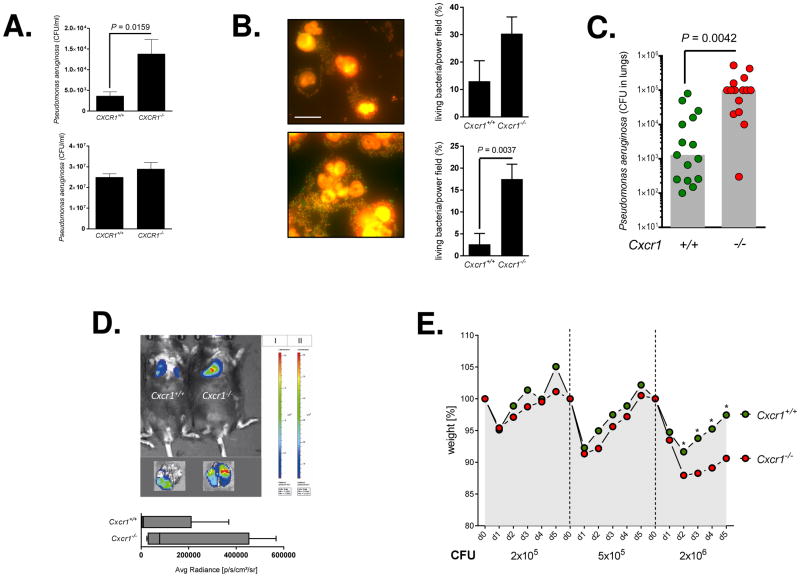
Fig. 1. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections.
(A) Upper panel: intracellular killing / Lower panel extracellular killing: Bone-marrow-isolated neutrophils from age- and sex-matched Cxcr1+/+ and Cxcr1−/− mice were infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PAO1) for 60 minutes at MOI50 and CFUs were counted. Data from n=5 independent experiments (means, SEMs) are shown.
(B) GFP-Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PAO1) bacteria and bone-marrow-isolated neutrophils from age- and sex-matched Cxcr1+/+ and Cxcr1−/− mice were co-incubated for 7 or 60 minutes at MOI50. Bacteria were stained using a live/dead bacterial staining kit (left panel) and quantified microscopically (right panel). Representative images of Cxcr1+/+ (upper left panel) and Cxcr1−/− (lower left panel) neutrophils 60 minutes after GFP-Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PAO1) infection (MOI50) are shown. Living bacteria are shown in green, dead bacteria in red. The scale/size bar represents 10μm. Bars show percentages of living bacteria at 7 minutes (upper right panel) and 60 minutes (lower right panel) at MOI50. Data from n=5 independent experiments (means, SEMs) are shown.
(C–E) Age- and sex-matched Cxcr1+/+ and Cxcr1−/− mice were infected intranasally (C, E) or intratracheally (D) with Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PAO1 all except for D, luciferase-expressing TBCF10839 isogenic mutant D8A6) and lung CFU (C), bacterial lung in vivo clearance (D) and weight loss (E) were monitored. For these experiments, 2×106 CFU (C), 5×107 (D) or 2×105 – 2×106 CFU PAO1 bacteria (E) were inoculated. (C) bars represent medians; CFUs were quantified in lungs 12 hours after the infection; (D) Bioluminescence imaging was performed 24 hours after the infection for n=5 (Cxcr1+/+) or n=4 (Cxcr1−/−) independent experiments; box and whiskers (range: min/max, quartiles, medians) are shown; (E) mean weight points are shown. * P < 0.05 Cxcr1+/+ versus Cxcr1−/− mice.