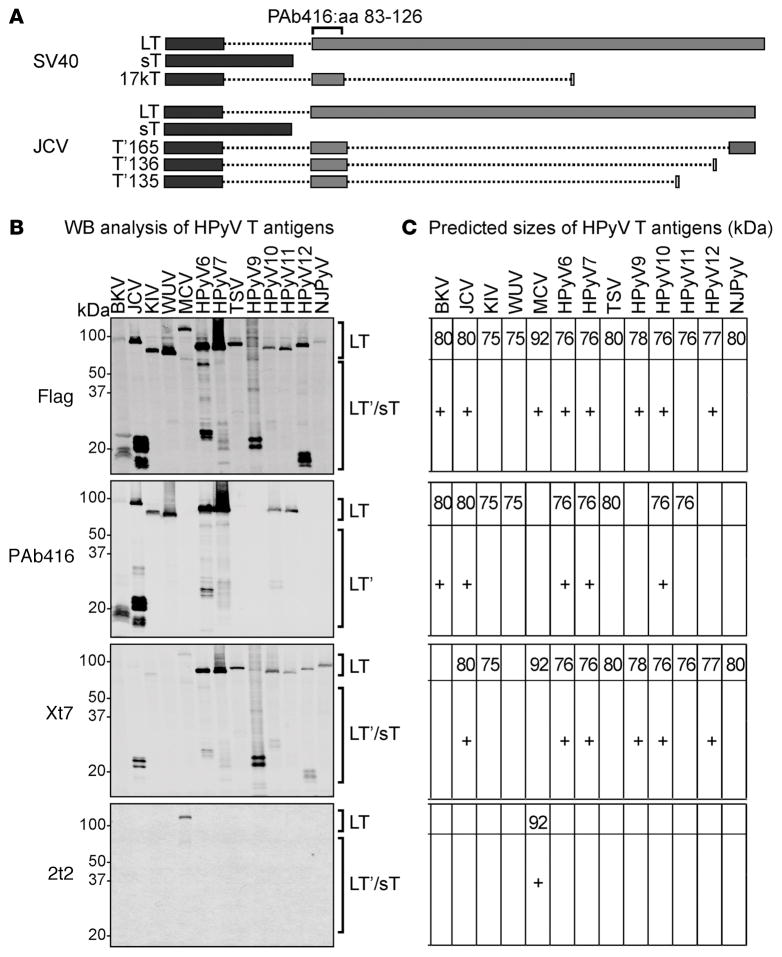
Figure 1. Detection of human polyomavirus early region proteins in HEK293 cells.
(A) Splicing arrangement of simian virus 40 (SV40) and JC virus (JCV) T antigens. Rectangles indicate the coding sequences: dark gray rectangles represent exon 1 and the light gray rectangles represent exon 2. Dotted lines represent the intron sequences. The PAb416 diagnostic antibody recognizes an epitope within aa 83–126 of exon 2 that is conserved in most of the human polyomaviruses (HPyVs). Different splicing events in JCV T antigen give rise to truncated forms of large T (LT), including T’165, T’136, and T’135. (B) Early gene expression of HPyVs was analyzed by Western blotting (WB) using anti-Flag, PAb416, Xt7, or 2t2. Observed sizes of LT from different HPyVs vary between 75 and 125 kDa. HPyV T antigen splice variants are between 15 and 60 kDa (HPyV T antigen splice variants are indicated by a plus sign in C). PAb416 antibody detects early proteins from BKV, JCV, KIV, WUV, HPyV6, HPyV7, TSV, HPyV10, and HPyV11. Xt7 antibody detects early region proteins from HPyV6, HPyV7, TSV, HPyV9, HPyV10, HPyV11, HPyV12, and NJPyV and detects KIV, MCV, and JCV splice forms weakly. 2t2 antibody detects MCV LT and the 57 kDa T. (C) The predicted sizes of HPyV T antigens (in kDa) are shown for respective immunoblots. sT, small T; BKV, BK virus; JCV, JC virus; KIV, KI virus; WUV, WU virus; MCV, Merkel cell polyomavirus; TSV, trichodysplasia-spinulosa virus; NJPyV, New Jersey polyomavirus.