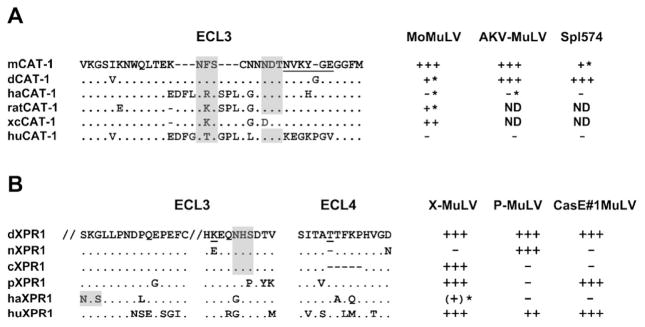
Figure 5.
Amino acid sequences of the extracellular loops (ECLs) of CAT-1 and XPR1 that contain MuLV receptor determinants. (A) Sequences represent NIH 3T3 (mCAT-1), M. dunni (dCAT-1), hamster (haCAT-1), rat (ratCAT-1), rat XC cell (xcCAT-1), and human (huCAT-1) [55, 93, 94]. (B) Sequences represent M. dunni (dXPR1), NIH 3T3 (nXPR1), M. castaneus (cXPR1), M. pahari (pXPR1), hamster (haXPR1), and human (huXPR1) [28, 92]. Shown are residues 416–430 and 499–508 in ECL3. Relative susceptibilities are given on the right for 3 E-MLVs for CAT-1 and for 3 X/P-MLVs for XPR1; asterisks identify infections that can be enhanced by inhibitors of N-linked glycosylation. Critical residues in CAT1 and XPR1 are underlined; N-linked glycosylation sites are shaded. ND, not done.