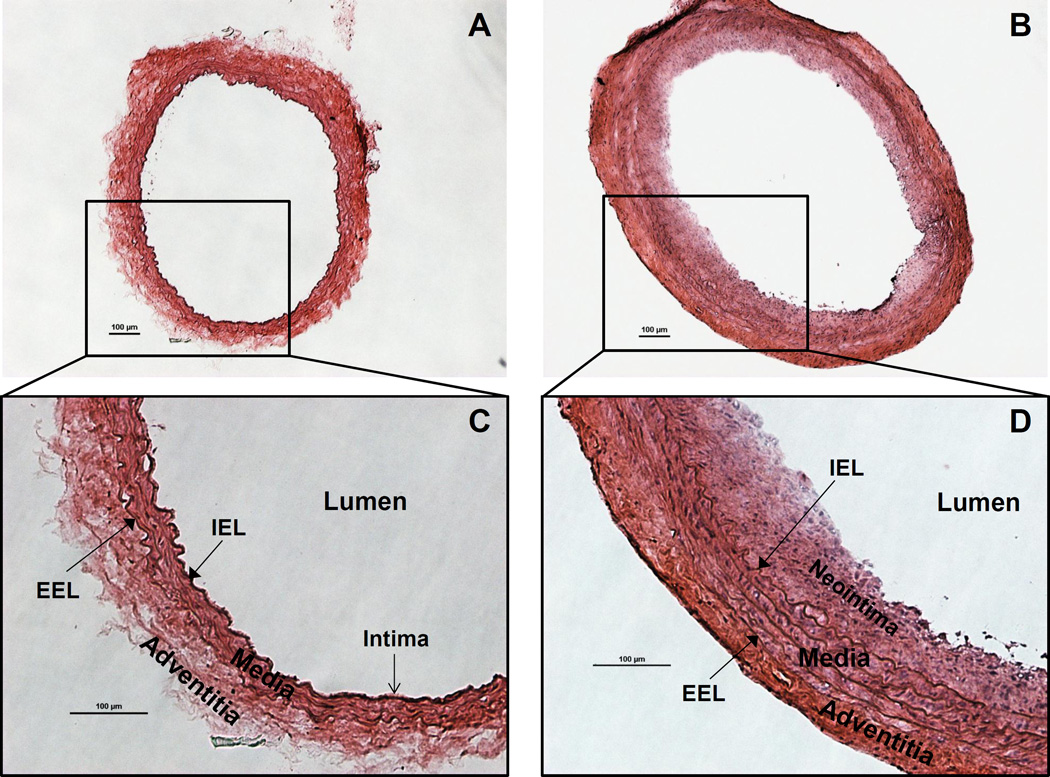
Figure 1.
Rat carotid artery cross sections stained with Hematoxylin & Eosin (H&E). A. Morphology of the normal/intact (right) CCA. B. Morphology of the injured (left) CCA, showing neointima formation and adventitia/media thickening. C. Structure of the normal rat carotid artery wall. The intima is a monolayer of endothelial cells lining on the internal elastic lamina (IEL). Media is the smooth muscle cells and elastic tissues between IEL and external elastic lamina (EEL). Adventitia is the outer layer. D. Rat carotid artery wall robust thickening 2 weeks after injury. Smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration lead to neointima formation and media thickening. Typical concentric neointima formatted and media/adventitia thickened, showing successful generation of balloon injury phenotype. The red (eosin) staining is enhanced in adventitia, due to robust collagen synthesis. Scale bars are 100µm.