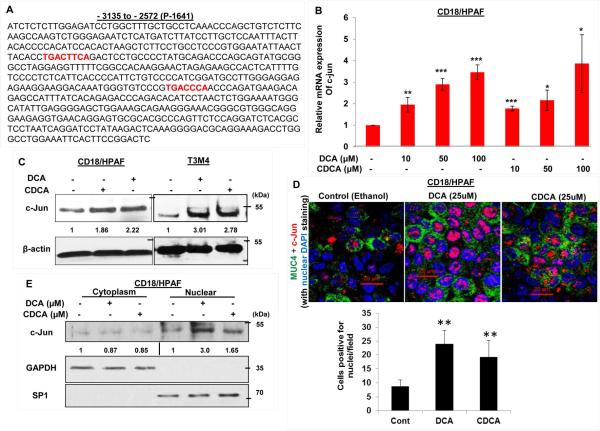
Figure 4. The effects of BA on MUC4 expression via activation and nuclear translocation of c-Jun.
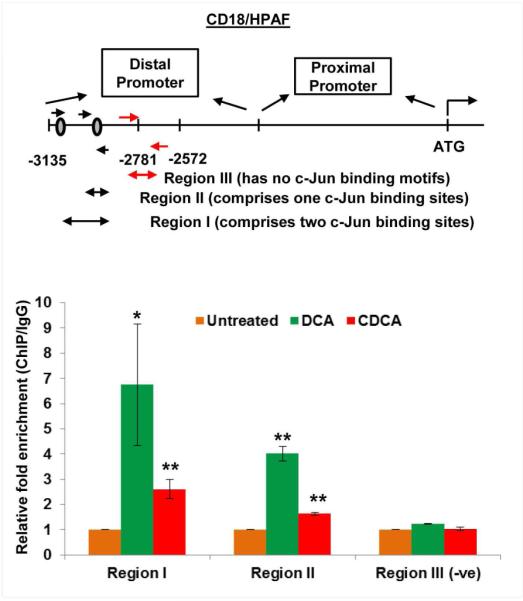
A. Sequence of the MUC4 distal promoter (P-1641) which has two binding sites for c-Jun protein (marked red). B. Graph showing increase in c-Jun mRNA expression in a dose-dependent manner in CD18/HPAF cell line, treated for 2 h with DCA and CDCA. C. CD18/HPAF and T3M4 cell lines were treated with BA (50 μM) for 4 h and cell lysates were collected. Immunoblot was performed to observe change in c-Jun expression in DCA- and CDCA-treated CD18/HPAF and T3M4 cell lines, compared to their respective untreated controls. D. Confocal images showing significant increase in c-Jun and MUC4 protein expression in CD18/HPAF cells treated with DCA or CDCA. Graph showing the quantification of the c-Jun positive nuclei in DCA and CDCA treated CD18/HPAF cells. E. Immunoblot showing significant increase in the expression levels of c-Jun in the nuclear fraction obtained from BA (25 μM)-treated CD18/HPAF cells, whereas cytoplasmic fraction did not demonstrate any noticeable alteration in c-Jun expression. F. ChIP experiment was performed to observe the effect on enrichment for c-Jun binding on MUC4 distal promoter in the presence or absence of DCA (50 μM) and CDCA (50 μM). We observed a significant increase in fold-enrichment at both region-I (containing two c-Jun binding sites) and region-II (containing one c-Jun binding sites). (*p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001, scale bar = 20 μM)