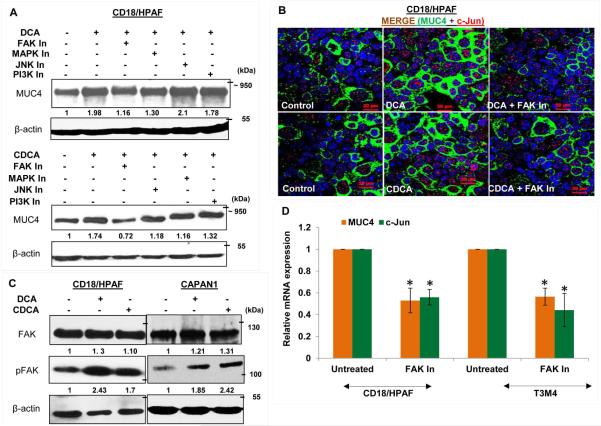
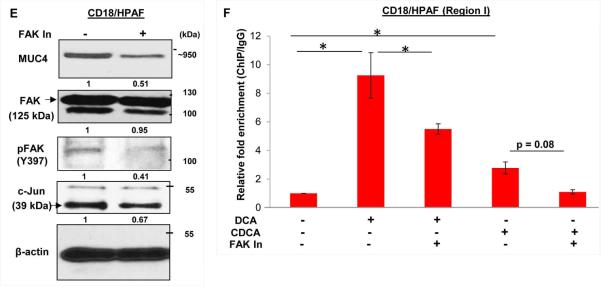
Figure 5. BA-mediated upregulation of MUC4 is dependent on FAK activation.
A. Concomitant treatment of 25 μM of DCA or CDCA in the presence or absence of selective pharmacological signaling inhibitors for 12h led us to know that the FAK pathway is mainly responsible for MUC4 upregulation upon BA exposure, as attenuation of this pathway maximally suppresses the BA-mediated upregulation of MUC4, compared to the other signaling inhibitors. Besides FAK, inhibiton of MAPK pathway also led to reduced MUC4 expression. B. Images obtained from immunofluorescence experiment showing MUC4 upregulation in DCA (25 μM) and CDCA (25 μM) treated CD18/HPAF cells, which is attenuated upon inhibiting FAK activity (or phosphorylation). C. Increase in FAK activity was confirmed by analyzing pFAK (Tyr397) expression upon BA (25 μM) treatment of CD18/HPAF and CAPAN1 cell lines for 4h. D. Graphical representation of relative mRNA expression for MUC4 and c-Jun gene altered upon inhibition of FAK pathway in both CD18/HPAF and T3M4 cell lines. E. Immunoblot showng that inhibition of FAK pathway, using 15 μM of FAK Inhibitor 14, leads to downregulation of MUC4, pFAK and c-Jun in CD18/HPAF cells. F. Graph representing the relative fold enrichment for c-Jun on AP-1 sequence motifs present on MUC4 distal promoter when CD18/HPAF cells were concomitantly treated with DCA and CDCA in the presence and absence of FAK inhibitor for 4 hours. (*p<0.05, scale bar = 20 μM)