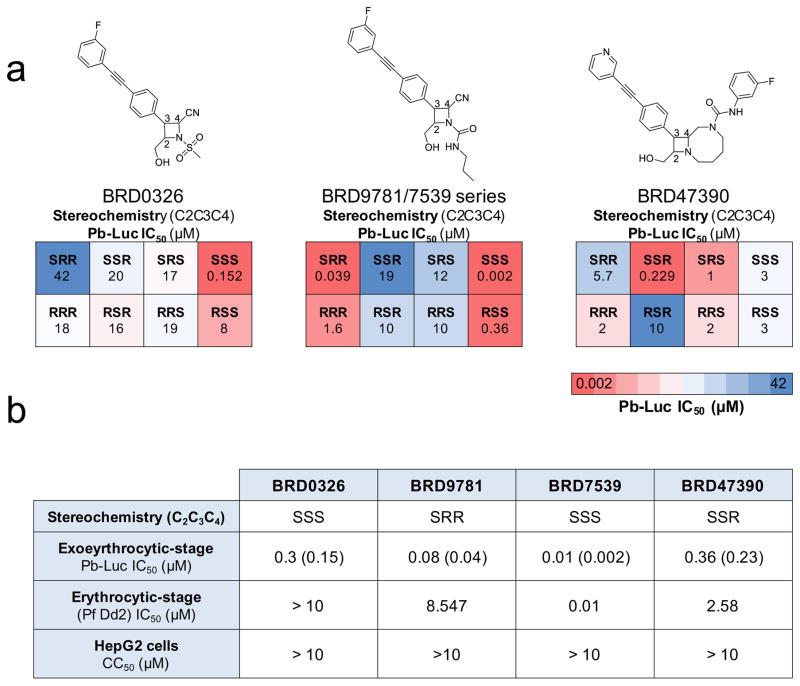
Figure 4. DOS compounds exhibit stereoselective inhibition of Pb-Luc exoerythrocytic-stage parasite growth.
a) Representative compounds and activity profiles with activity against P. berghei in HepG2 cells. Stereocenters (Cn) are listed below the corresponding chemical structure. Pb-Luc exoerythrocytic-stage activity was measured for each of the 8 possible stereoisomers (SRR, SSR, SRS, SSS, RRR, RSR, RRS, and RSS) of each compound. Three of the eight possible stereoisomers of BRD9781 have exoerythrocytic-stage activity, two with potent activity (SRR and SSS, IC50 <0.1 μM), and another with moderate activity (RSS, IC50 < 1 μM). B. One stereoisomer of BRD0326 (SSS) is active (IC50 < 1μM). C. Two stereoisomers of BRD47390 have significant exoerythrocytic-stage activity (SSR, IC50 < 0.1 μM; SRS, IC50 < 0.1 μM).
b) Compounds were tested in dose in the P. berghei/HepG2 assay, a Dd2 erythrocytic stage assay, and in a mammalian cell cytotoxicity assay. Compounds from three scaffold libraries are shown. Compounds were tested twice in the exoerythrocytic-stage assay; values from the second assay are shown in parentheses.