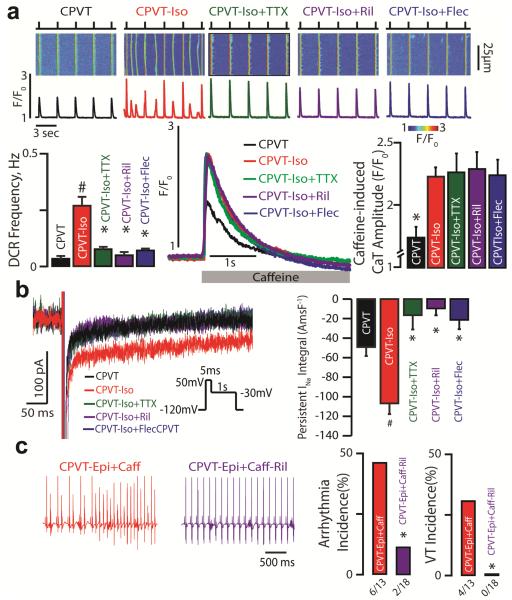
Fig. 1. β-AR simulation increases propensity for CPVT by augmenting TTX-sensitive nNav-mediated late INa.
(a) Effect of β-AR stimulation on nNav blockade and Ca2+ handling. (Top) Representative examples of the line-scan images and corresponding Ca2+ transients (CaT) recorded in CPVT ventricular cardiomyocytes loaded with Ca2+ indicator, Fluo-4FF AM and paced at 0.3 Hz. Cells were treated with isopreteranol (Iso, 100 nM) and tetrodotoxin (TTX, 100 nM), riluzole (Ril, 10 μM) or flecainide (Flec, 2.5 μM). β-AR stimulation with Iso promotes DCR events in the form of Ca2+ waves relative to untreated CPVT cardiomyocytes (n=166 and 34 cells, respectively; #, p<0.001 Wilcoxon rank-sum test). TTX, Ril and Flec significantly decreased DCR frequency in CPVT cardiomyocytes exposed to Iso (n =109, 48 and 66 cells, p<0.001 Kruskal-Wallis test; *, p=0.003, p<0.001 and p=0.032 Wilcoxon rank-sum test for TTX, Ril and Flec vs. ISO, respectively). (Bottom) Representative caffeine-induced (20 mM) CaT. ISO significantly increased caffeine-induced CaT relative to untreated CPVT cardiomyocytes (n = 13 and 11 cells, respectively; *, p=0.005 Wilcoxon rank-sum test). This elevation in caffeine-induced CaT persisted despite concomitant treatment with TTX, Ril and Flec (n = 11, 13 and 10 cells, respectively, p = 0.99 Kruskal-Wallis test). (b) Effect of β-AR stimulation and subsequent nNav blockade on persistent INa. Representative traces of persistent INa elicited using the protocol shown in the inset. Iso enhanced persistent INa in CPVT cardiomyocytes (n = 18 and 21 cells, respectively; #, p=0.004 Wilcoxon rank-sum test). This response to Iso was completely abolished upon addition of TTX, Ril or Flec (n = 9, 7 and 9 cells, respectively, p<0.001 Kruskal-Wallis Test; *, p<0.001 Wilcoxon rank-sum test for each treatment groups vs. ISO). Summary data presented as persistent INa integral amp-msec/F (AmsF−1). (c) Effect of β-AR stimulation on nNav-mediated ventricular arrhythmias in vivo. Representative ECG recordings of CPVT mice after catecholamine challenge with intraperitoneal injection (i.p.) of epinephrine (1.5 mg/kg) and caffeine (120 mg/kg; red ECGs). A subset of mice was pretreated with Ril (15 mg/kg; purple ECGs). Arrhythmia and ventricular tachycardia (VT) incidence (%) in CPVT mice exposed to catecholamine challenge during Na+ channel blockade with riluzole (n = 13 vs 18 CPVT-Epi+Caff vs CPVT-Epi+Caff-Ril treated mice. *, p=0.043 and *, p=0.023 Fisher's exact test for Arrhythmia and VT incidence, respectively).