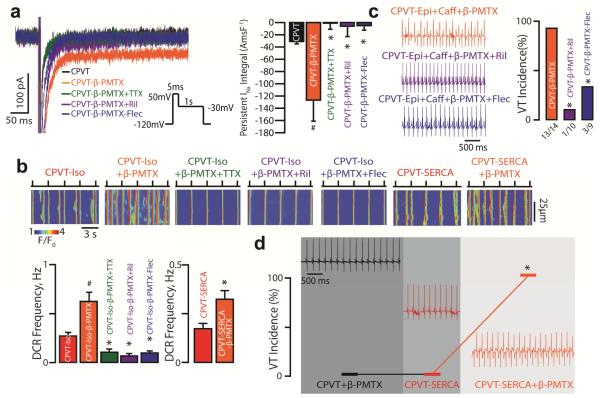
Fig. 2. TTX-sensitive nNav-mediated persistent INa augmentation in conjunction with increased SR Ca2+ load contribute to CPVT.
(a) Slowed inactivation of nNav with β-PMTX results in TTX-sensitive persistent INa in CPVT mice. Representative traces of persistent INa recorded in CPVT cardiomyocytes. Direct augmentation of nNav-mediated persistent INa with β-PMTX (40 μM) in CPVT myocytes increased persistent INa relative to control (n =12 and 31 cells, respectively, # p=0.004 Wilcoxon rank-sum test). β-PMTX-induced persistent INa was reduced by 100 nM TTX, 10 μM Ril and 2.5 μM Flec (n = 8, 6 and 5 cells, p < 0.001 Kruskal-Wallis test; *, p=0.002, p=0.039, p=0.003 Wilcoxon rank-sum test vs β-PMTX alone, respectively). (b) Pharmacological augmentation of nNav-mediated persistent INa promotes DCR in CPVT. Representative line-scan images obtained from CPVT cardiomyocytes and those conditionally overexpressing SERCA2a (CPVT-SERCA) that were loaded with Ca2+ indicator, Fluo-3 AM and paced at 0.3 Hz. Concomitant application of Iso (100 nM) and β-PMTX (40 μM) further promoted DCR frequency in CPVT cardiomyocytes relative to CPVT myocytes exposed to Iso alone (n = 79 and 166 cells, respectively, # p=0.001 Wilcoxon rank-sum test). Addition of TTX (n =38), Ril (n = 61) or Flec (n = 70) significantly reduced Iso/β-PMTX-promoted DCRs (p < 0.001 Kruskal-Wallis test; *, p<0.001 Wilcoxon rank-sum test for each experimental group vs.ISO+β-PMTX). In the absence of catecholamines, CPVT-SERCA cardiomyocytes exposed to β-PMTX evidenced greater DCR frequency relative to the untreated ones (n = 80 and 83 cells, respectively;*, p=0.01 Wilcoxon rank-sum test). (c) Representative ECG recordings of CPVT mice after catecholamine challenge with i.p. injection of epinephrine (1.5 mg/kg) and caffeine (120 mg/kg) and pretreatment with, β-PMTX (30mg/kg), β-PMTX+Ril (15 mg/kg) or β-PMTX+Flec (20 mg/kg). VT incidence in CPVT mice exposed to catecholamine challenge during various interventions (n = 14, 10 and 9 mice for CPVT-β-PMTX, CPVT-β-PMTX+Ril and CPVT-β-PMTX+Flec, respectively. * p<0.001 and p=0.005 Fisher's exact test for CPVT-β-PMTX vs. CPVT-β-PMTX+Ril and CPVT-β-PMTX vs. CPVT-β-PMTX+Flec, respectively). (d) Representative ECG recordings and summary VT incidence of CPVT+SERCA mice before and after doxycycline-induced SERCA2a overexpression and in the presence or absence of β-PMTX (30mg/kg; n = 6, *p = 0.031 McNemar’s test for CPVT-SERCA vs. CPVT-SERCA+β-PMTX). All experiments in CPVT-SERCA mice were conducted in the absence of epinephrine and caffeine. Before induction of SERCA2a overexpression all 6 mice were exposed to β-PMTX. After 2-3 weeks of doxycycline-supplemented diet, all 6 mice (horizontal line connecting the hash marks that represent VT incidence) were assessed for arrhythmias after which they were again exposed to β-PMTX.