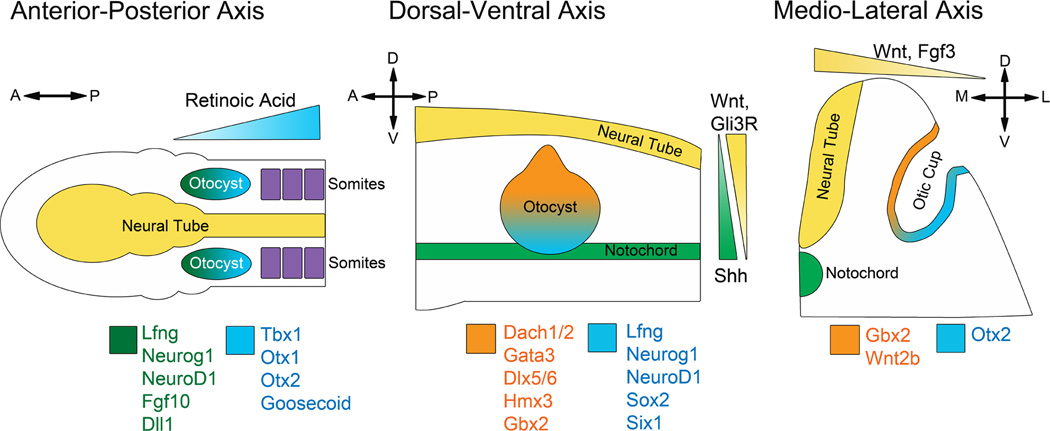
Figure 2.
Cardinal axis determination of the amniote inner ear. As the otic placode invaginates to form the otic cup and eventually closes to form the otocyst, the earliest axes established are the medio-lateral axis and the anterior-posterior axis, with the dorsal-ventral axis determined shortly afterwards. A posterior source of retinoic acid provides a gradient that allows for the expression of posterior and anterior otic genes. The neural tube provides a source of Wnt to create a dorsalizing gradient and is these dorsalizing signals are augmented by a gradient of inhibitory Gli3R, while the notochord sets up a gradient of Shh, establishing a ventral character. During the otic placode and otic cup stages, Wnt and Fgf3 gradients from the neural tube help establish a medial and a lateral identity.