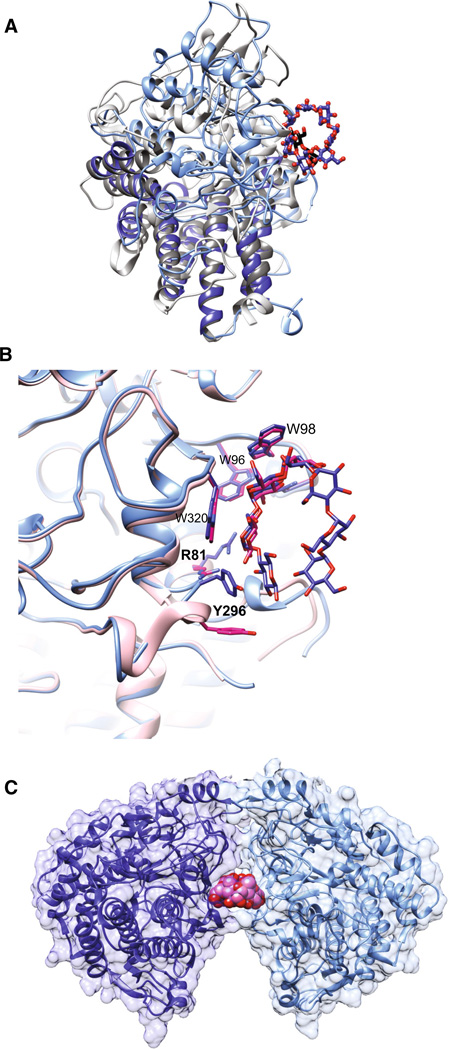
Fig. 2.
Molecular structure of SusD with maltooligosaccharides. a Superposition of SusD (blue, PDB 3CK9) with bound maltoheptaose (blue sticks) and the SusD homolog BT1043 (gray, PDB 3EHN) that targets mucosal glycans with bound N-acetyllactosamine (black sticks). The conservation of the eight tetratricopeptide repeat helices is highlighted in darker colors for both proteins. The RMSD for these proteins is 2.8 Å over 324 aligned residues (12.6 % sequence identity). b Superposition of the structure of SusD with bound maltoheptaose (blue) and maltotriose (pink), highlighting the plasticity within the binding site. Residues that move upon binding of a longer α-glucan are in bold print. c SusD crystallized with α-cyclodextrin revealed protein dimerization. The affinity of starch-binding to the cell surface may be enhanced by an avidity effect, whereby multiple SusD proteins cooperate to bind the polymer