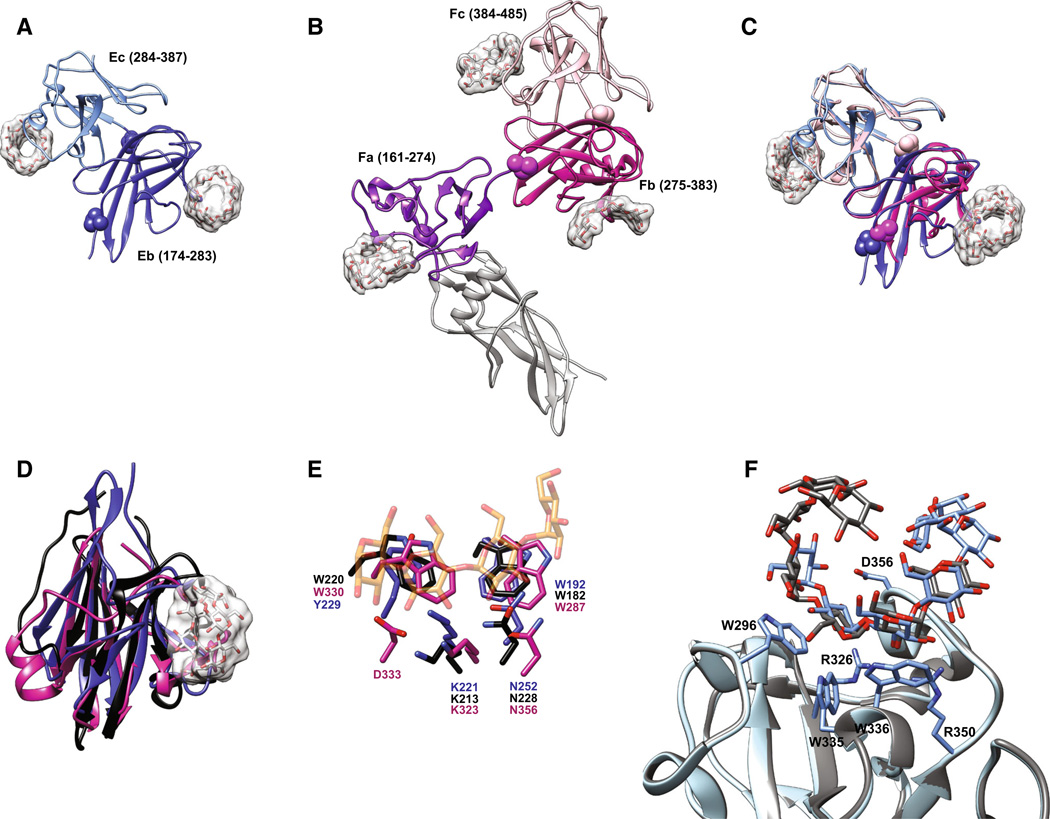
Fig. 4.
Structures of the SusE and SusF proteins. a Structure of SusE with bound α-cyclodextrin (PDB 4FEM), with the starch-binding domains Eb and Ec in different colors. Proline residues between the domains are highlighted as spheres. b Structure of SusF with bound maltoheptaose (PDB 4FE9), with the starch-binding domains Fa, Fb, and Fc in different colors. Proline residues between domains are highlighted as spheres. c Overlay of the Eb/Ec and Fb/Fc domains of SusE and SusF, colored as in panels a and b. d Superposition of the Eb domain (blue), Fb domain (pink) and the X25 domain (black, residues 161–270 of PDB 2WAN) from the Bacillus acidopullulyticus pullulanase [76]. e Close-up of the starch-binding sites in Eb and Fb from the overlay in panel d, demonstrating that these residues are conserved within the X25 module of the pullulanase (PDB 2WAN). Residues and labels are colored as in panel d, and the portion of the αcyclodextrin bound to Eb is displayed as transparent orange and red sticks. f Overlay of the two positions that maltoheptaose occupied at the Ec binding site of SusE (PDB 4FCH), demonstrating how a longer single-helical stretch of amylose could be accommodated