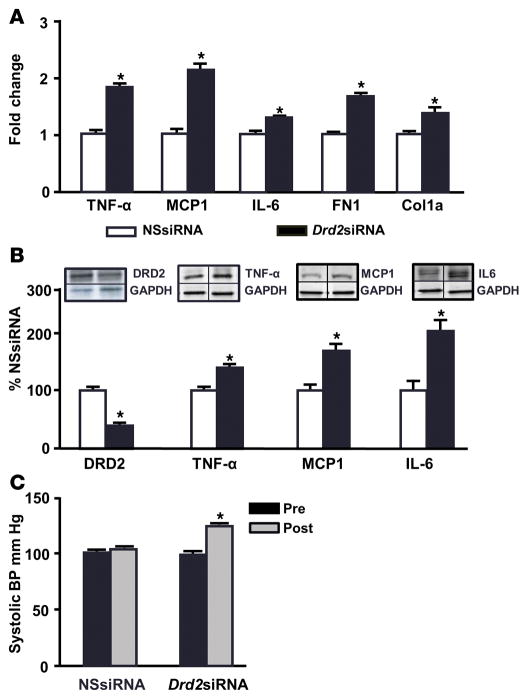
Figure 3. Renal Drd2 silencing increases the expression of proinflammatory factors and blood pressure.
Mice were treated with nonsilencing siRNA (NSsiRNA) or dopamine receptor D2 (Drd2) siRNA by right renal subcapsular infusion via osmotic minipump for 28 days. (A) Renal cortical mRNA expression of TNF-α, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP1), IL-6, fibronectin 1 (FN1), and collagen type 1a1 (Col1a1) was quantified by qRT-PCR. GAPDH mRNA was used for normalization of the data. n = 5–6/group, *P < 0.05 vs. NSsiRNA, Student’s t test. (B) Renal cortical protein expression of DRD2 (55 kDa), TNF-α (25 kDa), MCP1 (17 kDa), and IL-6 (25 kDa) was determined by immunoblot. One set of immunoblots is shown. Relative abundance of the proteins was normalized to GAPDH and expressed as a percentage of the NSsiRNA-treated group. n = 3–6/group, *P < 0.05 vs. NSsiRNA, Student’s t test. (C) Systolic blood pressures measured under pentobarbital anesthesia in mice before (Pre) and 28 days after (Post) siRNA infusion. n = 5–6/group, *P < 0.05 vs. all others, 1-way ANOVA and Tukey test.