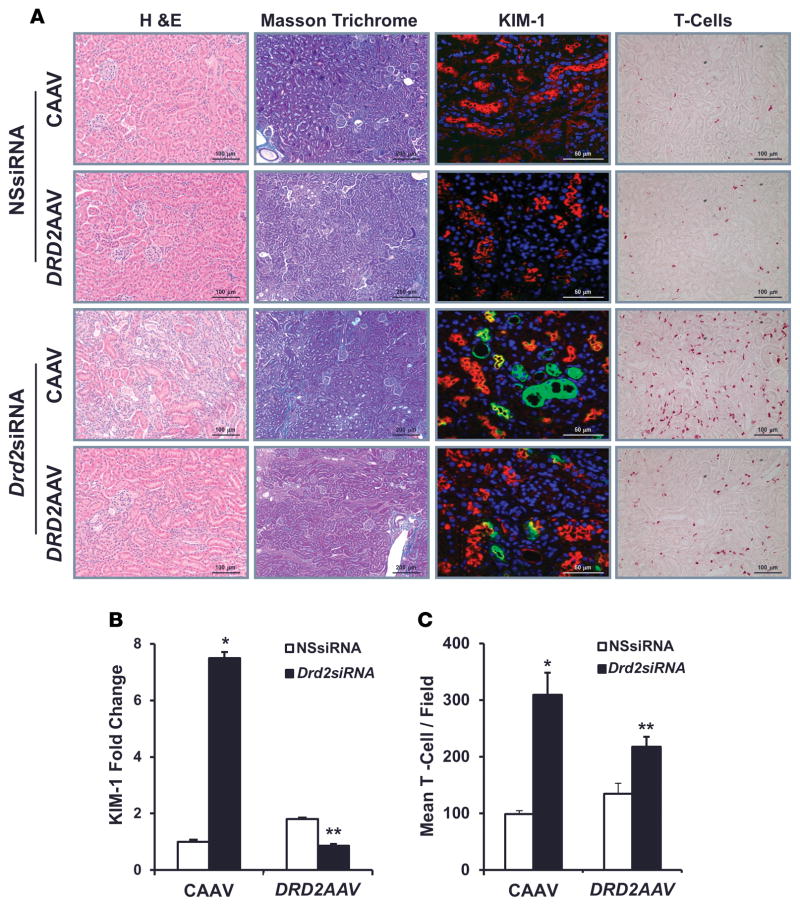
Figure 6. Rescue of DRD2 expression minimizes the renal injury induced by Drd2 silencing.
Twenty-eight days after left renal subcapsular infusion of siRNA and following left ureteral retrograde adeno-associated virus (AAV) treatment from day 14 to day 28, the mice were euthanized. Kidney sections from the indicated groups were stained with (A) H&E for morphology (scale bar: 100 μm) and Masson’s trichrome for collagen deposition (scale bar: 200 μm). These stains demonstrated areas of cortical scarring, appearing as clusters of smaller, atrophic tubules in association with increased intertubular connective tissue. Immunofluorescence/confocal microscopy for Ki-67 protein (scale bar: 50 μm) showed the proliferating renal tubule cells and T cells (scale bar: 100 μm). Quantification of (B) kidney injury molecule-1-positive (KIM-1-positive) cells and (C) T cells in the indicated kidney sections. n = 3/ group. *P < 0.05 vs. all others, **P < 0.05 vs. CAAV+Drd2 siRNA group, 1-way ANOVA and Tukey test. DRD2, dopamine D2 receptor; NSsiRNA, nonsilencing siRNA.