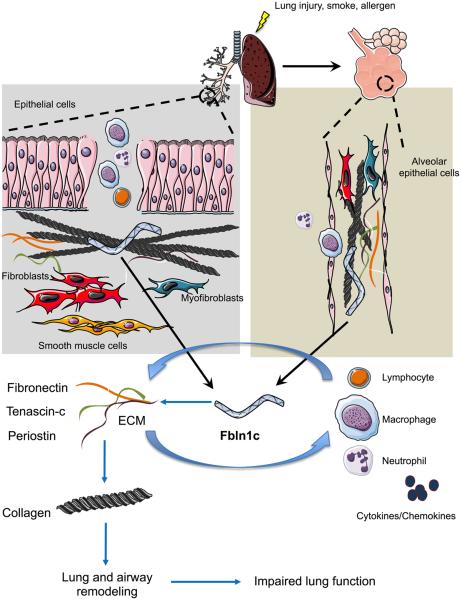
Figure 8. Schematic diagram of the role of Fbln1c in lung remodeling and inflammation.
Lung injury, smoke, or allergen exposure increases Fbln1c in airways and parenchyma. This stabilizes fibronectin, tenascin-c, and periostin and promotes collagen deposition. Excess collagen deposition induces lung and airway remodeling and impaired lung function. Fbln1c also promotes airway inflammation — involving the influx of macrophages, neutrophils, and lymphocytes — and increases in associated cytokines/chemokines that induce the production of ECM proteins and the development of respiratory disease.