Fig. 3.
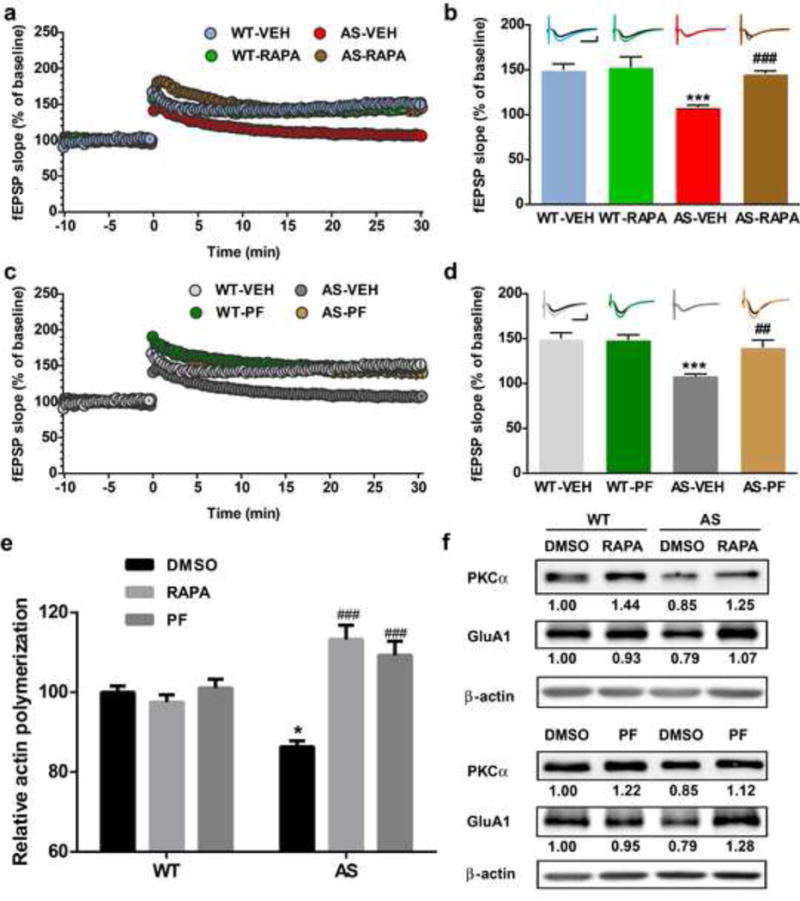
Effects of acute rapamycin or PF-4708671 treatment on LTP, actin polymerization and PKCα and GluA1 levels in hippocampus slices of WT and AS mice. (a) Reversal of LTP impairment in AS mice by acute rapamycin (50 nM) treatment. Slopes of fEPSPs were normalized to the average values recorded during the 10 min baseline. (b) Means ± S.E.M. of fEPSPs measured 30 min after TBS in different groups. N = 3–5 slices from 3–5 mice. Insert shows representative traces of evoked fEPSPs before and 30 min after TBS. Scale bar: 0.5 mV/10 ms. (c) Reversal of LTP impairment in AS mice by acute PF-4708671 (5 μM) treatment. Slopes of fEPSPs were normalized to the average values recorded during the 10 min baseline. (d) Means ± S.E.M. of fEPSPs measured 30 min after TBS in different groups. N = 3–5 slices from 3–5 mice. Insert shows representative traces of evoked fEPSPs before and 30 min after TBS. Scale bar: 0.5 mV/10 ms. (e) Effects of rapamycin (50 nM) and PF-4708671 (5 μM) treatment on actin polymerization in hippocampal slices from WT and AS mice. Data represent means ± SEM from 3 mice. (f) Representative images and quantitative analysis of Western blots labeled with PKCα, GluA1 and β-actin antibodies in P2 fractions of WT and AS hippocampal slices treated with vehicle, rapamycin or PF-4708671. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001, as compared to vehicle-treated WT slices, and ##p<0.01, ###p<0.001, as compared to vehicle-treated AS slices, two-way ANOVA with Newman-Keuls post-test
