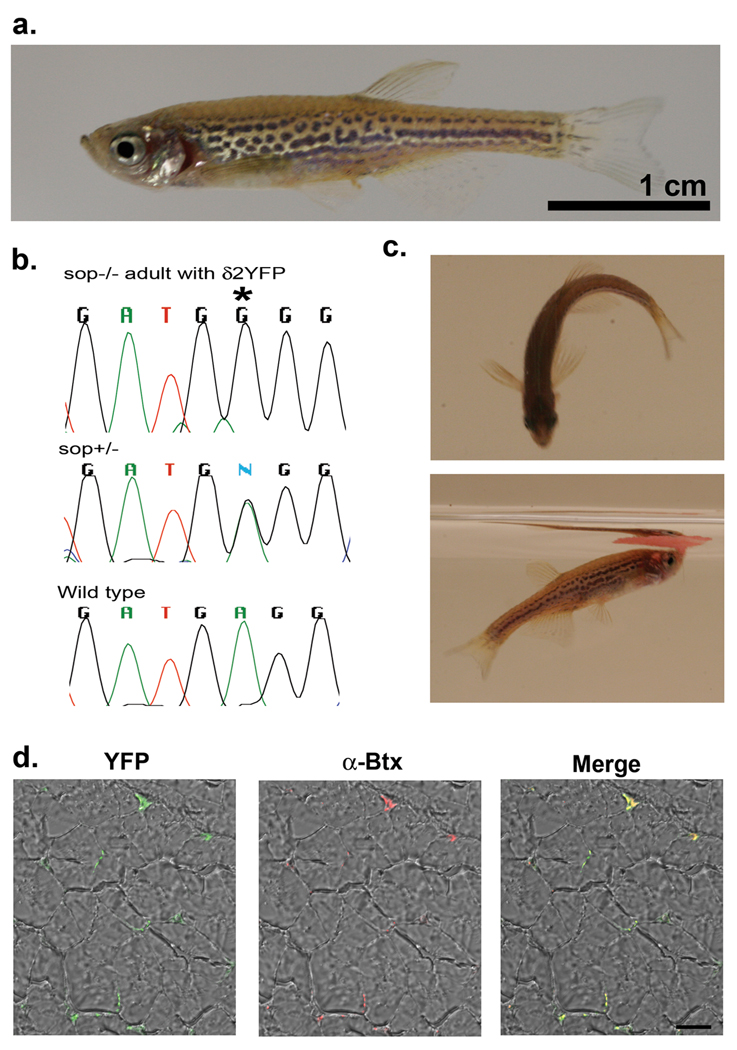
Figure 6.
a. A 1 year-old δ2YFP/sop−/− fish. The fish is anatomically indistinguishable from wild type fish. Scale: 1 cm.
b. The δ2YFP/sop−/− fish was genotyped with BccI and direct sequencing. The chromatogram of sequencing results is shown, which is complementary to the coding strand. This fish shows G at the critical site (marked with an asterisk; top), whereas a heterozygous fish shows a mixture of A and G (middle), and a wild type fish shows A (bottom).
c. Behaviors of a δ2YFP/sop−/− fish. In the upper panel, it is making a C-bend. In the lower panel, it is eating a flake of food on the water surface.
d. YFP fluorescence detected from a transverse section of muscle in δ2YFP/sop−/− fish. The left panel is a merged image of the YFP signal and transmitted light. The middle panel is a merged image of the α-Btx signal and transmitted light. The right panel is the merged image of all signals.