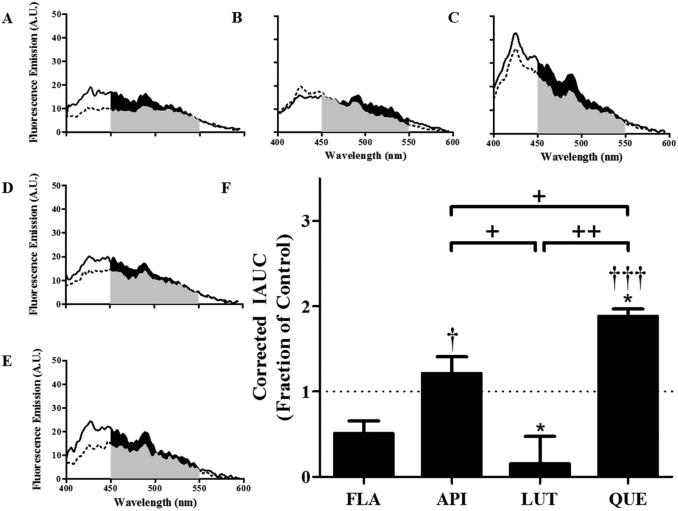
Figure 3. Hydroxylated anthoxanthins alter Aβ oligomer surface hydrophobicity.
Oligomers were prepared from Aβ1-42 (15 μM) in the absence (CONT, panel A) or presence of 150 μM anthoxanthins flavone (FLA, panel B), apigenin (API, panel C), luteolin (LUT, panel D), or quercetin (QUE, panel E), as described in Figure 2. Resulting oligomer products were diluted (15-fold) into 100 μM ANS, and fluorescence (emission: 400-600 nm; excitation: 350 nm) was measured for samples (solid line) and corresponding blanks (anthoxanthin, ANS) (dashed line). KAE self-fluorescence prohibited evaluation of ANS binding to oligomers made in the presence of this anthoxanthin. F) Fluorescence values were determined as the IAUC from 450-550 nm with blank subtraction. Corrected fluorescence was normalized to the control, shown as a dashed line with a value of 1 and representing no change. Error bars indicate SEM, n=3-4. *p<0.05 versus control; †p<0.05 and †††p< 0.001 versus flavone; +p<0.05 and ++p<0.01 between samples.