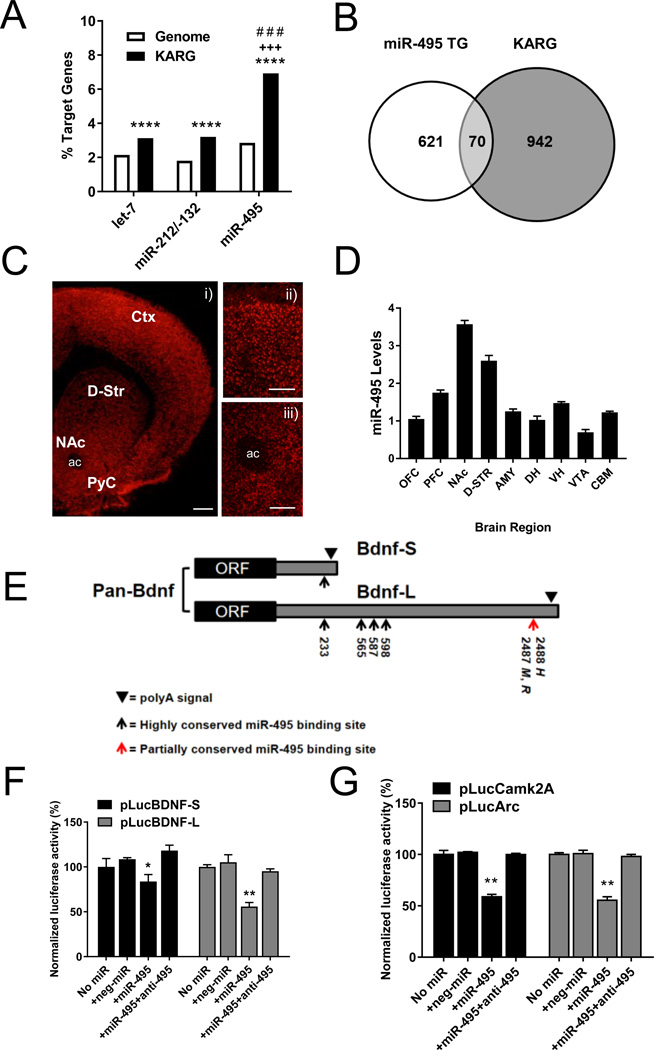
Figure 1. miR-495 targets several addiction-related genes (ARGs) and is expressed in addiction-related brain regions.
(A) Although the frequencies of miR-495, miR-212/132 and let-7 putative targets are all enriched in the KARG database compared to the entire genome, the frequency of miR-495 targets in KARG is significantly higher (~2-fold) than those of miR-212/132 and let-7. ****p < 0.0001 vs. genome, +++p < 0.001 miR-495 vs. miR-212/132 and # # # p< 0.001 miR-495 vs. let-7, two-tailed Chi square test. (B) Number of genes with putative miR-495 target sites (miR-495 TG) in the mouse KARG set. (C) Representative images of a coronal mouse brain section where miR-495 was visualized using fluorescent in situ hybridization at 4× (i), with insets at 10× focusing on the PFC (ii) and the NAc (iii). Scale bars 500 µm in panel i and 200 µm in ii and iii. (D) qRT-PCR analysis of miR-495 levels in different brain regions (n = 3). (E) Schematic representation of the short and long 3’UTR transcripts of BDNF including the positions of conserved and partially conserved miR-495 binding sites (M = Mus musculus, R = Rattus norvegicus, H = Homo sapiens). For in vitro target validation, HeLa cells were transfected with a firefly luciferase reporter containing the 3’UTR of Bdnf and Camk2a. A Renilla vector was co-transfected with the firefly reporter. Pre-miR-495, anti-miR-495 and pre-miR™ miRNA precursor negative control #2 were transfected as described in Supplementary Information. The alternative 3’UTRs of BDNF (F), as well as the 3’UTRs of Camk2a and Arc, were assayed (G). n = 4 *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Error bars indicate SEM. Ctx = neocortex, PyC = pyriform cortex, ac = anterior commissure. OFC = orbitofrontal cortex, PFC = prefrontal cortex, NAc = nucleus accumbens, D-STR = dorsal striatum, AMY = amygdala, DH = dorsal hippocampus, VH = ventral hippocampus, VTA = ventral tegmental area, CBM = cerebellum.