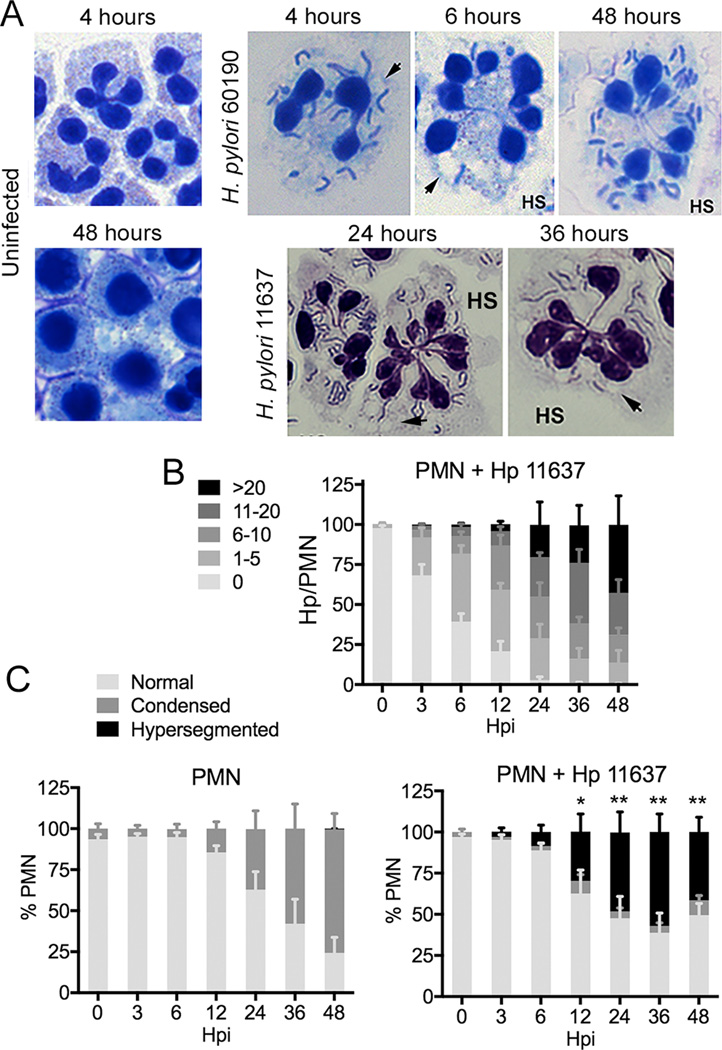
FIGURE 1.
H. pylori accumulates in human neutrophils and induces nuclear hypersegmentation. (A) Microscopy images of control PMNs and cells that were infected with H. pylori strains 11637 or 60190 for the indicated amounts of time. Data shown are representative of 8 or more independent experiments. Arrowheads indicate vacuoles. HS indicates hypersegmented cells. (B) Bacterial load in infected PMNs. Data are the mean + SEM (n = 4). (C) PMN nuclear morphology was scored as normal (3–5 lobes), condensed (1–2 lobes), or hypersegmented (6 or more lobes). Data are the mean + SEM (n = 4). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. 0 h hypersegmentation.