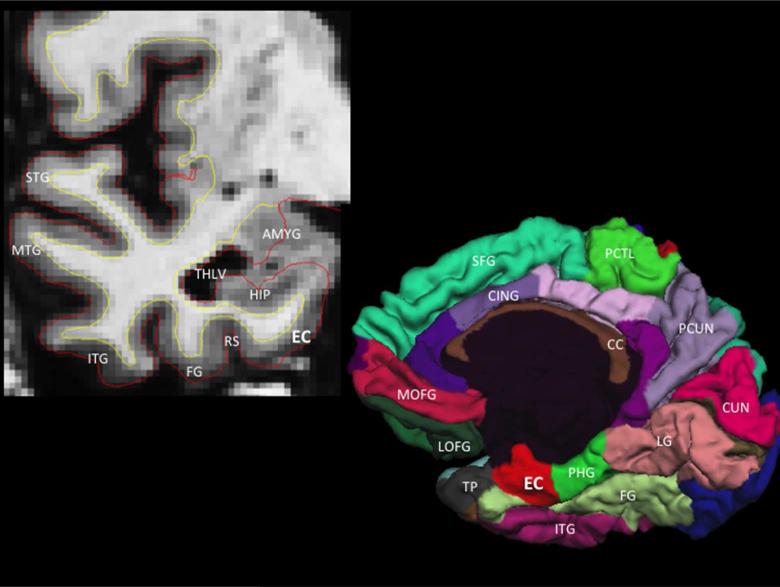
Figure 1.
Coronal T1-weighted MRI illustrating the anatomic location of the entorhinal cortex (EC), which is medial to the rhinal sulcus (RS) and fusiform gyrus (FG) and inferior to the hippocampus (HIP), temporal horn lateral ventricle (THLV) and amygdala (AMYG) (top left panel). Three-dimensional cortical (pial) representation of the right cortical (pial) surface delineating the location of the entorhinal cortex on the medial hemisphere of the cerebral cortex (bottom right panel). STG = superior temporal gyrus, MTG = middle temporal gyrus, ITG = inferior temporal gyrus, TP = temporal pole, PHG = parahippocampal gyrus, LG = lingual gyrus, CUN = cuneus cortex, PCUN = precuneus, FG = fusiform gyrus, PCTL = paracentral lobule, SFG = superior frontal gyrus, MOFG = medial orbitofrontal gyrus, LOFG = lateral orbitofrontal gyrus, CC = corpus callosum, CING = cingulate cortex.