Abstract
People typically drink alcohol to induce euphoria or reduce anxiety, and frequently drink in social settings, yet alcohol’s effect on human brain circuits involved in reward and emotion has been explored only sparingly. We intravenously administered alcohol to social drinkers while brain response to visual threatening and non-threatening social stimuli was measured using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). Alcohol robustly activated striatal reward circuits, while attenuating response to fearful stimuli in visual and limbic regions. Self-ratings of intoxication correlated with striatal activation, suggesting that activation in this area may contribute to subjective experience of pleasure and reward during intoxication. These results show that alcohol’s acute pharmacological rewarding and anxiolytic effects can be measured with fMRI.
Keywords: striatum, nucleus accumbens, alcohol, addiction, reward, amygdala
Behind only tobacco use and obesity, alcohol use is the third most common life style-related cause of death in the United States (Mokdad et al., 2004). People like to drink alcohol because of its ability to alter emotional states. Alcohol induces euphoria, relaxation, and disinhibition, while reducing stress, and anxiety. Consistent with human self-report, animal studies also suggest that alcohol produces a rewarding as well as an anxiolytic effect (Coop et al., 1990; Blanchard et al., 1993; Spanagel et al., 1995; Da Silva et al., 2005). Although its euphoric and stress reducing effects have been known for centuries and intuitively understood, how alcohol changes the function of human brain circuits has been explored only sparingly.
Where might alcohol recruit circuitry that regulates positive affect leading to euphoria? A critical area of interest is the ventral striatum (VS), which is recruited by reward-predictive stimuli (Knutson et al., 2001; Bjork et al., 2004). A variety of primary rewards activate this circuit, including fruit juice and water (Berns et al., 2001; O'Doherty et al., 2002; Pagnoni et al., 2002; McClure et al., 2003), as well as secondary rewards such as praise and money (see (Knutson and Cooper, 2005) for review). Similarly, functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies have shown striatal activation in response to drugs of abuse such as cocaine (Breiter et al., 1997) and nicotine (Stein et al., 1998). While there have not yet been fMRI studies of alcohol’s action on reward circuits, positron emission tomography (PET) studies demonstrate increased striatal glucose metabolism or blood flow in response to alcohol (Wang et al., 2000; Boileau et al., 2003; Schreckenberger et al., 2004). Accordingly, the mesocorticolimbic reward circuit is important in the development and maintenance of addiction (Koob et al., 1998).
How might alcohol affect circuitry that governs negative affect to decrease anxiety? Alcohol-mediated anxiolysis may result from disruption of threat detection circuitry. The amygdala in particular is critical in an attention allocation circuit that is recruited by stimuli that signal the requirement for an immediate behavioral response, such as fight or flight (LeDoux, 2003; Fitzgerald et al., 2006). Alcohol intoxication increases incidence of aggression and social risk-taking (Giancola and Zeichner, 1997; Corbin and Fromme, 2002; Giancola et al., 2002), perhaps by disrupting the amygdala-mediated differentiation between threatening and non-threatening stimuli. Decreased differential response may increase approach while decreasing avoidance, thus facilitating social interaction.
The current study was designed to characterize the brain’s response to alcohol intoxication and emotional stimuli, and is the first fMRI study to examine alcohol’s acute pharmacological effects on the neural circuitry underlying emotion. This study extends previous research by (1) using intravenous (IV) alcohol to minimize individual variability in alcohol pharmacokinetics and to maintain a steady-state of brain alcohol exposure; (2) using fMRI to measure the blood oxygenation-level-dependent (BOLD) signal during alcohol administration, (3) presenting emotional facial stimuli, which allows the use of a general linear model (GLM) to examine main effects for alcohol and emotional cues as well as their interaction, and (4) collecting subjective measures of intoxication to correlate with BOLD signal.
METHODS
Participants
Twelve community-recruited healthy social drinkers (7 women) participated in this study. All participants underwent a complete medical and psychiatric evaluation, including clinical laboratory, radiological and ECG examinations. Participants were excluded from the study if they had an abnormal physical exam or had laboratory values outside of normal ranges. Participants were given the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV diagnoses and were excluded if they met criteria for alcohol or other substance dependency (excluding nicotine) at any time, or if they fulfilled DSM-IV criteria for a current axis-I psychiatric disorder. Participants were also excluded if they had never consumed at least two standard drinks of alcohol within one hour, or if they reported to have a "facial flushing" response to the consumption of alcohol. They drank an average of 1.9 days per week (SD = 1.1) and an average of 3.6 drinks per drinking day (SD = 1.2).
Participants were all right-handed, average age 26.5 years (SD = 5.6), and none had ever had a head injury requiring hospitalization. They were instructed not to take any prescribed, non-prescribed, or over-the-counter medications in the 14-day period prior to the study visits. Additionally, participants were asked to abstain from alcohol for at least 3 days prior to each study visit. A urine sample was obtained from each participant during each study visit for a urine drug screen and for a pregnancy test in females.
Alcohol Infusion Procedure
Alcohol was infused as a 6%v/v solution in saline. The infusion rates were based on a physiologically-based pharmacokinetic model for alcohol (Ramchandani et al., 1999), consisting of an exponentially increasing infusion rate from the start of the infusion until the target breath alcohol concentration (BrAC) of 0.08 g% was reached at 15 min, followed by an exponentially decreasing infusion rate to maintain (or “clamp”) the BrAC at the target level. This infusion-rate profile was computed using individualized estimates of the model parameters, which are based on the participant’s height, weight, age and sex. This method has been used successfully in several studies of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacological effects of alcohol in humans (Kwo et al., 1998; Ramchandani et al., 1999; Ramchandani et al., 2001; Blekher et al., 2002; Morzorati et al., 2002; Ramchandani et al., 2002).
Experimental Design
This study consisted of three infusion sessions given on separate days, separated by at least 3 days. On each study session, participants reported to the NIH Clinical Center Day Hospital, where BrAC levels were measured and a urine drug screen and, in women, a urine pregnancy test, were performed. An IV catheter was inserted in each forearm; one was used for the infusion of alcohol or saline and the other for the collection of blood samples.
The first study session (familiarization session) took place in the Clinical Center Day Hospital. Participants received an alcohol infusion over 45 min, to ensure that they tolerated the alcohol infusion without experiencing nausea or marked sedation, prior to undergoing the infusions in the fMRI scanner during the second and third sessions. Serial breathalyzer measurements were obtained every 3–5 minutes from the start of the infusion using the Alcotest 7410 handheld breathalyzer (Drager Safety Inc., CO), to ensure that the BrACs were within 0.01 g% of the target and to enable minor adjustments to the infusion rates to overcome errors in parameter estimation and experimental variability (Ramchandani et al., 1999; O'Connor et al., 2000). Subjective response to alcohol was measured using the Biphasic Alcohol Effects Scale (BAES) (Martin et al., 1993) and the modified Drug Effects Questionnaire (DEQ), (de Wit and McCracken, 1990) which were given before the beginning of the infusion and every 10–15 minutes during the infusion. Mood ratings were obtained before the start and at the end of the infusion using the Positive and Negative Affect Scale (PANAS) (Watson et al., 1988). Blood samples (6 ml) were collected at three time-points: before the start of the infusion, and at 15 and 45 min after the start of the infusion. After the infusion was completed, BrAC measurements were taken every 30 min. Participants were sent home in a taxi cab when their BrAC dropped below 0.02 g%.
On the second and third study sessions, participants received the infusions in the scanner. One of these infusion was saline (placebo) and one was alcohol, given in a double-blind, randomized order during sessions 2 and 3. On these days, following IV catheter insertion, participants were placed in the scanner. A nurse was present in the scanning room throughout the infusion.
Structural scans were acquired as the infusion began. Target blood alcohol concentration (BAC) was expected to be achieved at 15 min, and emotional images were presented at 25 min as functional scans were acquired as described below. Participants were instructed to focus on the images, but no response was required. Blood samples (6 ml) were collected at three time-points: before the start of the infusion, at 15 min after the start of the infusion, and at 45 min, when the infusion ended. The DEQ was given at baseline, and before and after the set of images. Participants also completed the PANAS before and after the scan. The total duration of the infusion was 45 minutes, after which participants were escorted from the scanner and immediately given a breathalyzer test. They were then transported to the clinical unit, where BrAC measurements were taken every 30 min. Participants were sent home in a taxi cab when their BrAC dropped below 0.02 g%.
Stimuli
Visual images from a series of standardized emotional facial expression (EFE) images (Matsumoto, 1988) were used in this study. Forty-five neutral and 45 fearful faces, as well as a non-emotional control crosshair condition that served as the inter-stimulus interval, were presented in an event-related design that lasted 8 min 30 sec. The stimuli were each presented for 2 sec, and the ISI ranged from 0–8 sec. All stimuli were presented using a Linux laptop computer with in-house stimulus delivery software. They were projected using an Epson MP 7200 LCD projector onto a screen placed at the foot of the MRI scanner bed and were viewed using a mirror mounted on the head coil.
fMRI acquisition
Imaging was performed using a 3 T General Electric MRI scanner with a 16-channel head coil. Thirty contiguous 5.0 mm thick axial slices were acquired (in-plane resolution 3.75 mm × 3.75 mm), providing whole-brain coverage including subcortical regions of interest such as the nucleus accumbens (NAcc), as well as the prefrontal cortex including the VMFC (ventromedial frontal cortex) and OFC (orbitofrontal cortex), together with limbic areas (amygdala), anterior cingulate and the paralimbic areas and thalamus. Whole-brain high-resolution coronal structural scans were collected using a T1-weighted magnetization-prepared rapid gradient echo (MPRAGE) pulse sequence, which facilitated localization and co-registration of functional data (voxel size = 0.859 × 0.859 × 1.2 mm, matrix 256 × 256 × 124, repetition time (TR) = 100 ms, echo time (TE) = 12 ms, field of view (FOV) = 24 cm). Functional scans were acquired using a T2*-EPIRT sequence that measure changes in blood oxygen level dependent (BOLD) contrast (210 volumes, TR = 2s, TE = 30 ms, flip angle = 90, matrix 64 × 64, in-plane matrix = 128, FOV = 24 cm, slice thickness = 5 mm. BOLD images were collected during the presentation of the stimuli. Because of the short duration of the run, we did not do any band-pass filtering or de-trending of the data.
fMRI analysis
Analyses focused on changes in BOLD signal contrast (hereafter, activation) that occurred as the participants viewed the images following alcohol or placebo administration. Analyses were conducted using Analysis of Functional Neural Images (AFNI) software (Cox, 1996). Echoplanar image volumes were preprocessed as follows: (1) voxel time series were interpolated to correct for non-simultaneous slice acquisition within each volume (using sinc interpolation and the most inferior slice as a reference). (2) Volumes were corrected for motion in three-dimensional space. Motion-correction estimates indicated that no participant's head moved >1.0 mm in any dimension from one volume acquisition to the next. We imposed a 6 mm full-width half-maximum (FWHM) smoothing kernel in the spatial domain. (3) A mask was created so that all of the background values outside of the brain were set to zero. This allowed the calculation of the percentage signal change in each voxel. Statistical maps were generated for each individual separately by linear contrasts between the regressors of interest. The regressors of interest were the neutral and fearful EFE faces. Preprocessed time series data for each individual were then analyzed by multiple regression, which allowed co-variation of variables related to head motion. The regression model consisted of the orthogonal regressors of interest and six regressors of no interest modeling residual motion after volume registration. Regressors of interest were convolved with a gamma-variate function that modeled a prototypical hemodynamic response before inclusion in the regression model (Cohen, 1997). Idealized signal time courses were time-locked to image onset.
Anatomical maps of t statistics were spatially normalized by warping to Talairach space (Talairach, 1988) and combined into a group map. Next, a statistical map of the main effects of alcohol and facial emotion was computed by performing a voxel-wise ANOVA of the event-related β-coefficients calculated from the general linear model (using inputs of the regression model), In this three-factor mixed-model ANOVA, drug (alcohol or placebo) and emotion (fearful or neutral) were fixed factors, and subject was a random factor. Linear contrasts between the fearful and neutral conditions separately under the alcohol and placebo conditions (neutral: alcohol vs. placebo; and fearful: alcohol vs. placebo), as well as linear contrasts between the alcohol and placebo condition under each emotion type (alcohol: fearful vs. neutral; and placebo: fearful vs. neutral) were computed by performing voxel-wise t-tests between event-related β-coefficients of each stimulus type. When reporting ANOVA results, a family-wise error rate correction (using a Monte Carlo simulation) was applied to rule out false positives. When computing family-wise error-rate correction, statistical maps were resampled back into original voxel size. Clusters larger than 5 voxels at an individual voxel threshold level of p < 0.001 were considered significant. T statistics from the group maps were subsequently characterized by assessment of actual BOLD signal changes in volumes of interest.
Regions that have previously been implicated in either brain reward circuits (nucleus accumbens, putamen and caudate) or emotional-visual circuits (amygdala, fusiform gyrus, and lingual gyrus) were characterized with VOI analyses, in which time series signal data were analyzed. The VOIs were drawn as spheres with a radius of 5 mm, which was a small enough size to average signal data within the boundaries of small structures such as the NAcc and caudate, which were of a priori focus, and also allowed us to investigate the source of effects that were driving significant activations due to alcohol, emotional valence, or interactions in other cortical regions post-hoc. Signal data were extracted from the time series as follows: (1) signal at each voxel was converted to a (percentage) deviation from the mean for that voxel across the entire time series, (2) signal was averaged by stimulus type and spatially translated into Talairach space, and (3) a mask was created consisting of the volume of interest through which each individual participant's data was extracted. These data were subject to analysis of variance using the percent signal change in each region as the dependent variable and alcohol (alcohol or placebo), emotion (fearful or neutral), and the interaction between them as the independent variables (package JMP-SAS; SAS Institute, Cary, North Carolina). The p-value for significance (two-tailed) was set at 0.05. In cases of significant interactions, post-hoc t-tests were performed to evaluate differences between the conditions.
Correlational Analysis
Coefficients of association were computed for the magnitude of change in the VOI measures versus subjective measures of intoxication, as measured by the DEQ. For these analyses, the VOI measure was a BOLD “change score”, calculated as the average percent signal change to a stimulus class during the alcohol session minus the average percent signal change to the same stimulus class during the placebo session. A positive change score indicates that the participant exhibited a larger response during the alcohol condition, and a negative score indicates a larger response during the saline condition. Analysis was conducted using BOLD signal change under the neutral condition because this was the emotion type that demonstrated striatal activation.
RESULTS
Self-reported alcohol affects
All participants tolerated the infusion without complications. The average BrAC reached during the familiarization session was 0.070 mg% (SD = 0.008). All participants reported both stimulation and sedation effects on the BAES during this session. We saw the expected subjective effects of alcohol on the DEQ, with significant increases in high, intoxication, “feeling effects,” “liking” the drug, and “wanting more” of the drug, compared to baseline. Participants reported peak ratings of intoxication and feeling high at 25 min after the start of the infusion.
During the scanning sessions, the average blood alcohol concentration was 0.0 g% on the placebo day, and 0.072 g% (SD = 0.009) at the end of the infusion on the alcohol day. Participants were asked to report subjective feelings of intoxication and high using the DEQ every 10 min during the scans. None of the participants reported feeling any alcohol effects on the placebo day, and during the alcohol day, they reported peak intoxication from 25–45 min after the start of the infusion.
Participants did not differ significantly in self-report of positive or negative affect, measured by the PANAS, between the alcohol and the placebo day either before of after the scan. On the alcohol day, there was no change in negative or positive affect from pre- to post-scan, but on the saline day, participants reported a decrease in positive affect from pre- to post-scan (p = 0.003).
Neural activity
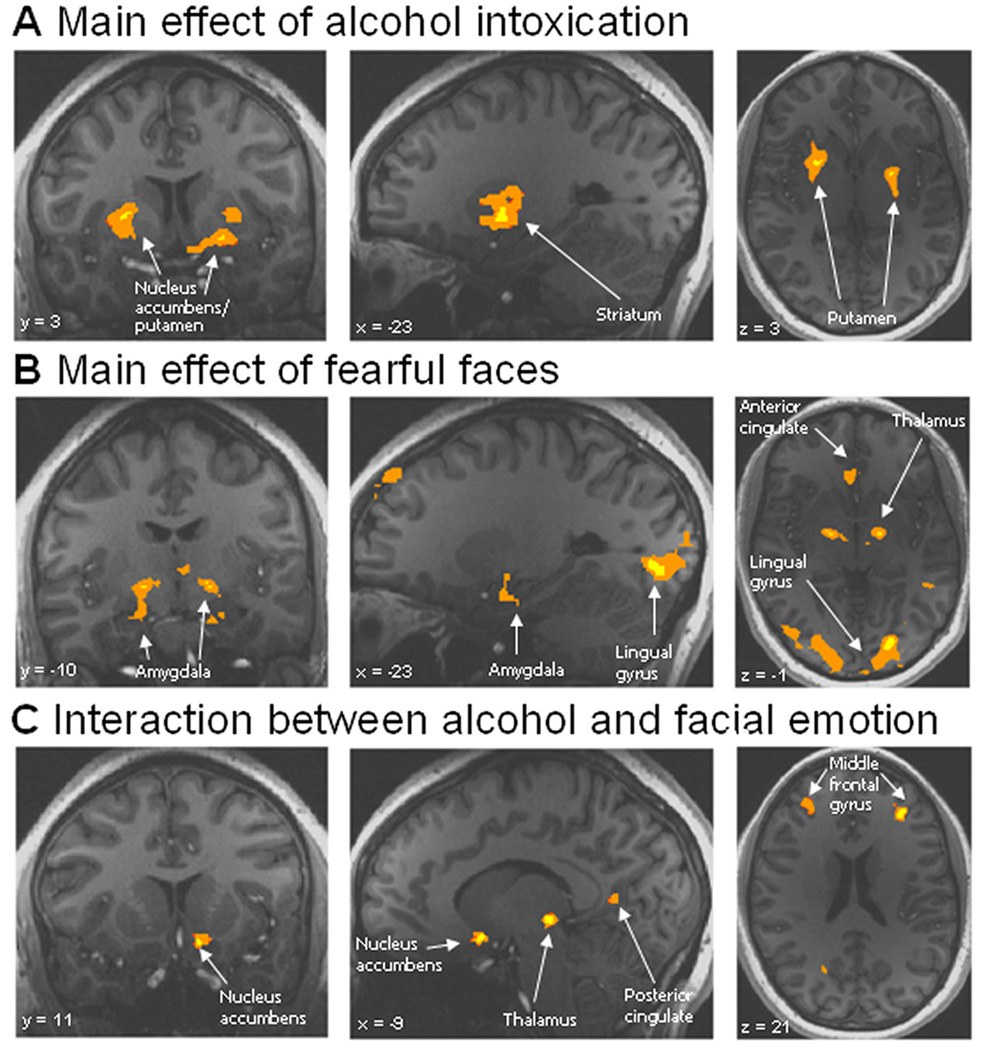
To test for the main effects of the alcohol and the facial emotion type, as well as the interaction between them, we used a GLM where alcohol (alcohol or placebo) and facial emotion (fearful or neutral) were fixed factors, and subject was a random factor. We found a significant main effect of alcohol intoxication on activation of VS across facial emotion types (Table 1; Fig 1A). Activation was also significant in the right parahippocampal gyrus, left precuneus, left anterior cingulate, and left superior temporal gyrus. Conversely, we found a significant main effect of facial emotion irrespective of alcohol administration in the right amygdala, bilateral lingual gyrus, left superior temporal gyrus, right superior temporal gyrus, and right anterior cingulate (Fig 1B). Significant interactions between alcohol and facial emotion were seen in the several regions, including the left insula, right lingual gyrus, left nucleus accumbens, and bilateral middle frontal gyri (Fig. 1C). These interactions were characterized in post hoc volume of interest analyses (Fig 3).
Table 1.
Main effects of alcohol and emotion, and their interaction, on brain response.
| Region | Talairach coordinates | Activated Volume | F value | p value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | (mm3) | |||
| Alcohol | ||||||
| Right Putamen | 23 | 5 | 6 | 5272 | 47.83 | < 0.0001 |
| Left Putamen | −23 | −1 | 0 | 3824 | 52.76 | < 0.0001 |
| Right Parahippocampal Gyrus | 23 | −45 | −10 | 1568 | 23.04 | < 0.001 |
| Left Precuneus | −15 | −43 | 40 | 1384 | 30.54 | < 0.001 |
| Left Anterior Cingulate | −17 | 25 | 24 | 696 | 22.19 | < 0.001 |
| Left Superior Temporal Gyrus | −57 | −5 | 4 | 560 | 24.22 | < 0.001 |
| Emotion | ||||||
| Left Lingual Gyrus | −23 | −77 | 0 | 4160 | 30.88 | < 0.001 |
| Right Amygdala | 17 | −9 | −2 | 3376 | 28.56 | < 0.001 |
| Left Superior Temporal Gyrus | −13 | 41 | 40 | 3208 | 24.82 | < 0.001 |
| Right Lingual Gyrus | 17 | −85 | −4 | 3088 | 22.57 | < 0.001 |
| Right Superior Frontal Gyrus | 13 | 45 | 36 | 776 | 22.91 | < 0.001 |
| Right Anterior Cingulate | 3 | 31 | −2 | 880 | 21.56 | < 0.001 |
| Interaction | ||||||
| Left Insula | −41 | −29 | −2 | 8392 | 32.08 | < 0.001 |
| Right Lingual Gyrus | 29 | −79 | −4 | 6528 | 42.02 | < 0.0001 |
| Left Medial Frontal Gyrus | −29 | 35 | 22 | 5368 | 50.44 | < 0.0001 |
| Right Posterior Cingulate | 19 | −63 | 16 | 2792 | 23.66 | < 0.001 |
| Right Inferior Frontal Gyrus | 61 | 11 | 24 | 2168 | 30.78 | < 0.001 |
| Right Superior Temporal Gyrus | 45 | −19 | 0 | 2152 | 28.16 | < 0.001 |
| Right Middle Frontal Gyrus | 31 | 41 | 20 | 1808 | 29.74 | < 0.001 |
| Left Posterior Cingulate | −11 | −57 | 12 | 1272 | 30.41 | < 0.001 |
| Left Thalamus | −9 | −25 | 0 | 1248 | 31.62 | < 0.001 |
| Left Middle Frontal Gyrus | −29 | 35 | 22 | 1168 | 50.44 | < 0.0001 |
| Left Nucleus Accumbens | −9 | 9 | −8 | 633 | 34.11 | < 0.001 |
Figure 1.
Main effect of (A) alcohol, (B) fearful facial emotion, and (C) the interaction between them on regional brain activation. Anatomical maps of t statistics were spatially normalized by warping to Talairach space and combined into a group map. Radiological convention is used to display left and right. A statistical map of the main effects of alcohol and facial emotion was computed by performing a voxel-wise ANOVA of the event-related β-coefficients calculated from the general linear model. In this three-factor mixed-model ANOVA, alcohol (alcohol or placebo) and emotion (fearful or neutral) were fixed factors, and subject was a random factor. Alcohol effects were seen primarily in striatal areas, while emotion effects were seen in limbic and visual processing areas. The color map represents the t-score; in orange regions, p < 0.01, and in yellow regions, p < 0.001. See Table 1 for values.
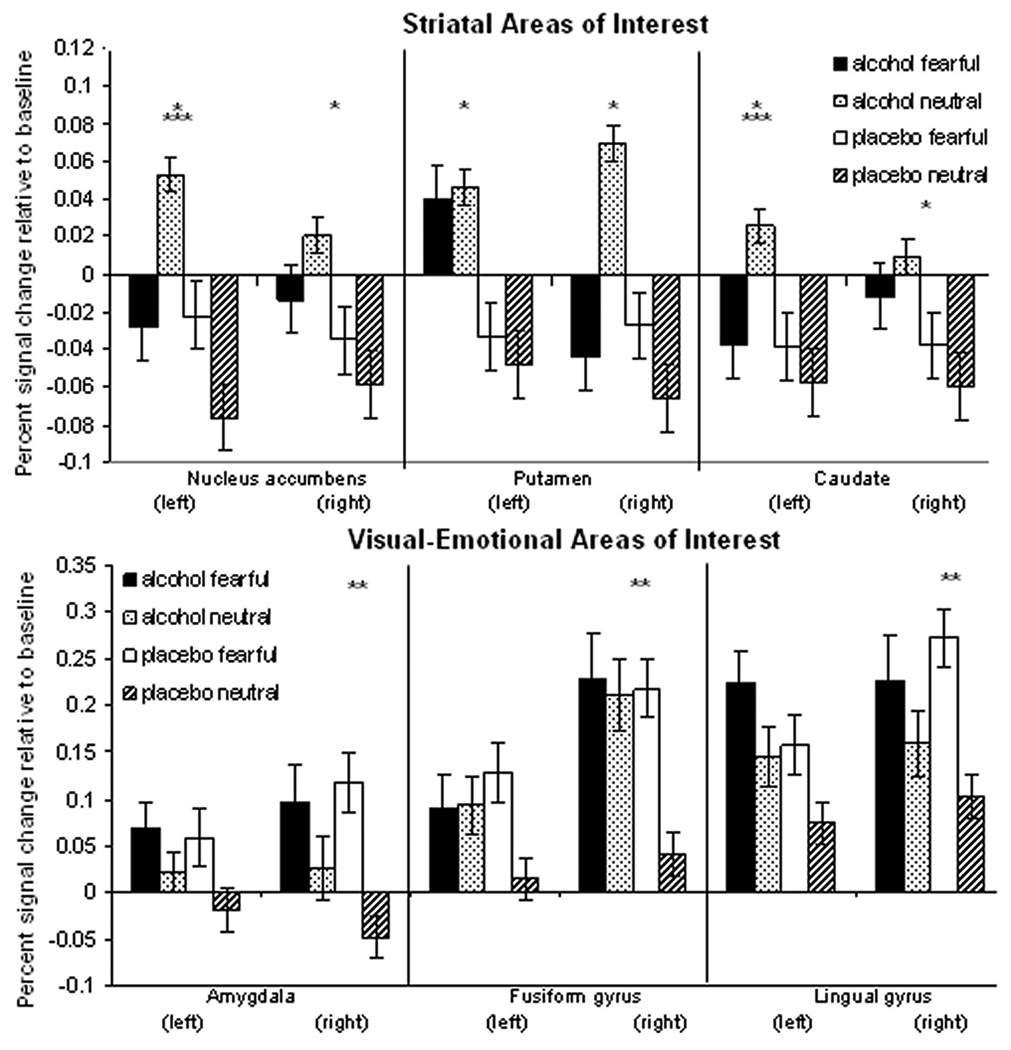
Figure 3.
Percent signal change in volumes of interest in each condition. Values were entered into the GLM to test for main effects of alcohol, emotion, and an interaction. * indicates a significant main effect of alcohol; ** indicates a significant main effect of facial emotion; *** indicates a significant interaction between alcohol and emotion. Striatal areas of interest showed significant alcohol effects, while visual-emotional areas showed significant effects of emotion. In the visual-emotional areas, alcohol decreased the difference between response to fearful and neutral faces. See Table 3 for values.
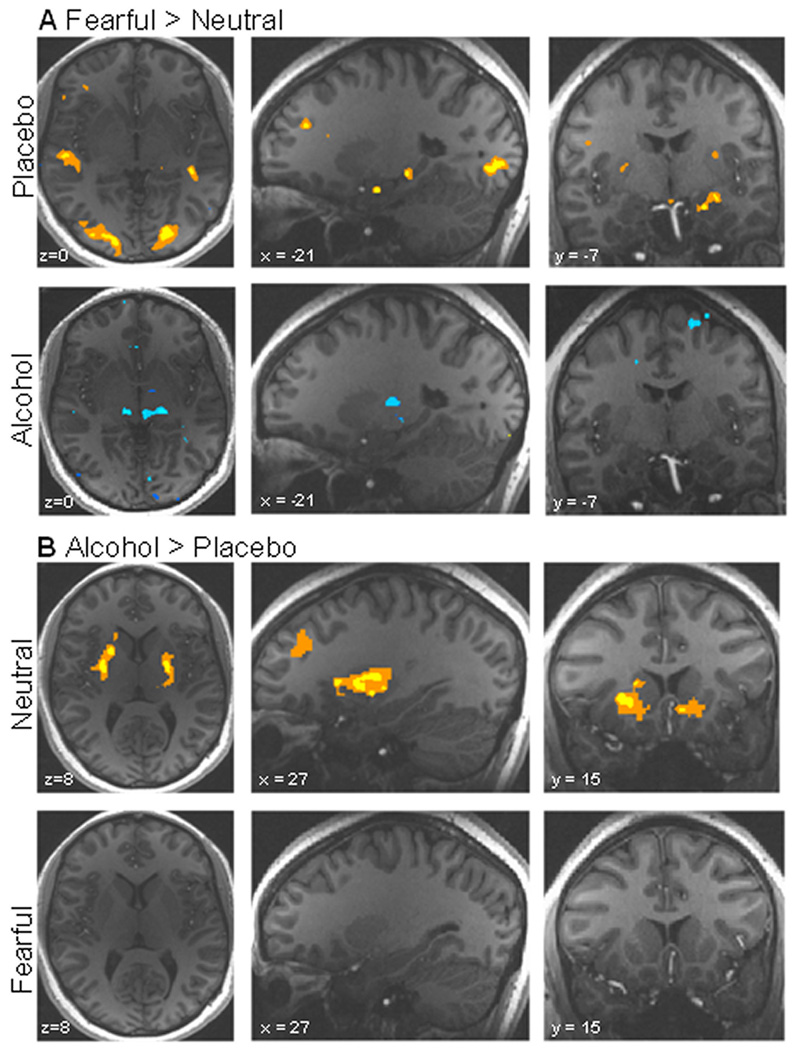
During the placebo infusion, fearful faces (in contrast with neutral faces) activated the amygdala, insula, and parahippocampal gyrus, as well as visual processing areas, with no regions showing greater activations to the neutral compared to fearful faces (Table 2; Fig. 2A). In contrast, when participants were intoxicated, the fearful faces did not elicit a larger response than the neutral faces in any region.
Table 2.
Brain activation by linear contrasts between each session and stimulus class.
| Region | Talairach coordinates | Volume | t-score | p value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | (mm3) | |||
| Neutral: Alcohol > Placebo | ||||||
| Left Putamen | −23 | −7 | 10 | 27504 | 8.57 | < 0.0001 |
| Right Putamen | 23 | 3 | 0 | 11472 | 7.63 | < 0.0001 |
| Right Superior Frontal Gyrus | 23 | 35 | 32 | 5392 | 5.56 | < 0.001 |
| Right Posterior Cingulate | 9 | −49 | 24 | 12432 | 5.55 | < 0.001 |
| Left Lingual Gyrus | −25 | −65 | −6 | 2312 | 4.69 | < 0.001 |
| Left Cingulate Gyrus | −17 | 23 | 28 | 1992 | 4.75 | < 0.001 |
| Neutral: Placebo > Alcohol | No clusters detected | |||||
| Fearful: Alcohol > Placebo | ||||||
| Left Putamen | −21 | 3 | −4 | 448 | 7.53 | < 0.0001 |
| Right Superior Temporal Gyrus | 49 | −3 | −10 | 456 | 5.19 | < 0.001 |
| Fearful: Placebo > Alcohol | ||||||
| Left Lingual Gyrus | −13 | −79 | −14 | 320 | 6.17 | < 0.0001 |
| Left Parahippocampal Gyrus | −41 | −33 | −4 | 552 | 4.69 | < 0.001 |
| Placebo: Fearful > Neutral | ||||||
| Left Amygdala | −21 | −9 | −14 | 3224 | 6.3 | < 0.0001 |
| Right Middle Frontal Gyrus | 57 | 23 | 22 | 2784 | 6.05 | < 0.0001 |
| Left Parahippocampal Gyrus | −21 | −27 | −4 | 728 | 5.64 | < 0.001 |
| Right Lingual Gyrus | 13 | −91 | 6 | 7296 | 5.62 | < 0.001 |
| Left Lingual Gyrus | −19 | −85 | 2 | 3056 | 5.55 | < 0.001 |
| Left Fusiform Gyrus | −37 | −41 | −12 | 5672 | 5.27 | < 0.001 |
| Right Anterior Cingulate | 9 | 13 | −8 | 952 | 5.23 | < 0.001 |
| Right Insula | 41 | −25 | −2 | 5440 | 4.9 | < 0.001 |
| Right Inferior Frontal Gyrus | 45 | −3 | 24 | 1744 | 4.89 | < 0.001 |
| Left Medial Frontal Gyrus | −21 | 37 | 24 | 1760 | 4.65 | < 0.001 |
| Left Medial Frontal Gyrus | −47 | 19 | 42 | 880 | 4.61 | < 0.001 |
| Placebo: Neutral > Fearful | No clusters detected | |||||
| Alcohol: Fearful > Neutral | No clusters detected | |||||
| Alcohol: Neutral > Fearful | ||||||
| Left Thalamus | −19 | −15 | 10 | 4544 | 5.22 | < 0.001 |
Figure 2.
Linear contrasts between the alcohol and placebo condition under each emotion type (alcohol: fearful > neutral; and placebo: fearful > neutral), as well as linear contrasts between the fearful and neutral conditions separately under the alcohol and placebo conditions (neutral: alcohol > placebo; and fearful: alcohol > placebo). These contrasts were computed by performing voxel-wise t-tests between event-related β-coefficients of each stimulus type. Radiological convention is used to display left and right. (A) Linear contrast between fearful vs. neutral faces in the alcohol and the placebo condition. Increased activation to negative faces is shown in yellow/orange (p < 0.01), while increased activation to neutral faces is shown in blue (p < 0.01). (B) Linear contrast between alcohol and placebo in the fearful and neutral condition. Increased activation to alcohol is shown in yellow/orange (p < 0.01), while increased activation to placebo is shown in blue (p < 0.01). See Table 2 for values.
Although we detected a main effect of alcohol intoxication in the striatum, this effect was primarily driven by the participants’ reaction to neutral, but not fearful, stimuli. Neutral faces elicited ventral striatum activation when subjects were intoxicated, but not when they were sober (Fig. 2B). Fearful faces elicited increased activation in the left putamen, but in a much smaller and more ventral region than in the neutral face condition.
Volume-of-interest analysis
We characterized BOLD signal changes in volumes of interest (VOIs) that have previously been implicated in either brain reward circuits (e.g. NAcc, putamen and caudate) or emotional-visual circuits (e.g. amygdala, fusiform gyrus, and lingual gyrus). Fearful faces elicited greater activation than neutral faces in the right-lateralized amygdala, fusiform gyrus, and lingual gyrus (Fig 3). Alcohol main effects were not statistically significant in these regions (see Table 3 for values). The alcohol × facial emotion interaction effect on amygdalar BOLD signal change reached trend level significance (p = 0.08). Pairwise simple effect t-tests clarified this trend, demonstrating that whereas fearful faces activated amygdala significantly more than did neutral faces (p < .05) during placebo infusion (as seen in both the time-series linear contrast maps, and in the extracted VOI data), while this effect was no longer significant (p > .10) during alcohol intoxication.
Table 3.
ANOVA results of volume-of-interest analyses in striatal and visual-emotional brain regions.
| Region | Alcohol | Emotion | Interaction | Alcohol | Emotion | Interaction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Striatal Regions | Visual-Emotional Regions | ||||||
| Right NAcc | F = 6.09 | NS | NS | Right amygdala | NS | F = 9.56 | F = 3.20 |
| (11, 10, −7) | p = 0.018 | (20, −5, −15) | p = 0.004 | p = 0.083 | |||
| Left NAcc | F = 8.63 | NS | F = 10.53 | Left amygdala | NS | NS | NS |
| (−11, 10, −7) | p = 0.005 | p = 0.002 | (−20, −5, −15) | ||||
| Right putamen | F = 14.27 | NS | NS | Right lingual gyrus | NS | F = 4.15 | NS |
| (24, 5, 6) | p = 0.0007 | (27, −79, −6) | p = 0.049 | ||||
| Left putamen | F = 15.11 | NS | NS | Left lingual gyrus | NS | NS | NS |
| (−24, 5, 6) | p = 0.0004 | (−27, −79, −6) | |||||
| Right caudate | F = 6.07 | NS | NS | Right fusiform | NS | F = 4.3 | F = 3.86 |
| (13, 17, −3) | p = 0.019 | (29, −56, −8) | p = 0.046 | p = 0.058 | |||
| Left caudate | F = 7.64 | NS | F = 5.41 | Left fusiform | NS | NS | NS |
| (−13, 17, −3) | p = 0.009 | p = 0.027 | (−29, −56, −8) |
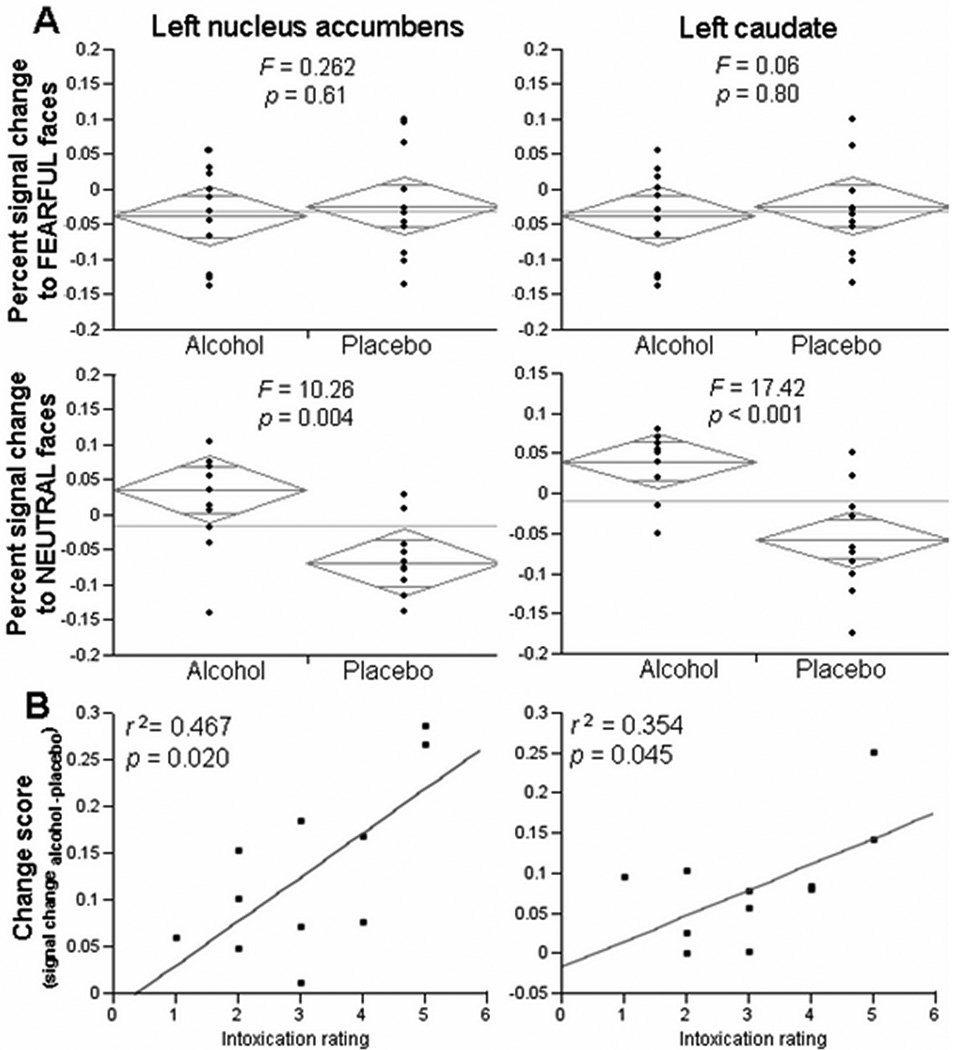
In the striatal VOIs, there were no main effects of emotion, but there were significant main effects of alcohol in the right NAcc, right caudate, right putamen, and left putamen, and significant interactions between alcohol and emotion in the left NAcc and the left caudate (Fig. 3; see Table 3 for values). In these two regions, post-hoc one-way comparisons indicated significant differences between the alcohol and the placebo condition when participants viewed the neutral faces, but no differences during the fearful face condition (Fig. 4A).
Figure 4.
(A) Where we observed significant interactions in the GLM (in the left NAcc and left caudate), we performed one-way ANOVAs. In these regions, there was a significant difference between the alcohol and the placebo condition when participants viewed the neutral faces, but no difference during the fearful face condition. (B) We ran a correlation between change scores, defined as percent signal change (to the neutral faces) during the alcohol session minus percent signal change (to the neutral faces) during the placebo session, and intoxication ratings measured by the DEQ. There was a significant association between change score and intoxication in the left NAcc and the left caudate.
Association between self-reported intoxication and neural activity
There was a significant positive association between subjective ratings of intoxication and BOLD change scores in the neutral facial expression condition in the left NAcc (r2 = 0.467, p = 0.020) and in the left caudate (r2= 0.354, p = 0.045). This indicates that participants who reported feeling more intoxicated showed a larger BOLD response to alcohol in these regions (Fig. 4B). Stepwise multiple regression indicated no effect of actual BAC levels, gender, or pre-scan mood ratings of negative or positive affect on BOLD activation. There was no correlation between subjective intoxication ratings and BAC levels, probably as a result of the minimal inter-subject variability in BAC using our ethanol infusion method. We also did not find the session order to have a significant effect in any of our analyses.
DISCUSSION
This study is the first to use fMRI to measure BOLD activation during intravenous alcohol infusion. The rapid IV administration of alcohol allowed us to achieve pharmacologically effective concentrations quickly, thus reducing acute adaptation and providing a clearer picture of alcohol’s direct effects. The results confirmed our expectation that alcohol would robustly activate striatal reward areas in the brain, especially the ventral striatum. Activation in the left NAcc and left caudate increased relative to baseline signal in conjunction with subjective ratings of intoxication. These findings confirm PET data indicating increased glucose utilization during alcohol administration in striatum (Wang et al., 2000; Boileau et al., 2003; Schreckenberger et al., 2004), and support Koob’s hypothesis that all drugs of abuse activate the striatum (Koob, 1992).
The anxiolytic effect of alcohol in visual-emotional brain areas
Despite alcohol’s use in social settings, there have been no previous human imaging studies examining interactions between alcohol and emotional cues. A variety of non-imaging human studies have attempted to experimentally alter emotional states while administering alcohol or measuring alcohol intake (Stritzke et al 1996; Gabel et al 1980; Curtin et al 1998; Schroder and Perrine 2007), but these studies have not demonstrated a specific anxiolytic interaction between alcohol and emotional cues. Alcohol can have vastly different effects on emotion depending on factors such as the point on the blood alcohol concentration vs. time curve, the individual’s drinking history, and the dose of alcohol consumed (Levenson et al., 1980; Lukas et al., 1986; Turkkan et al., 1988; Giancola and Zeichner, 1997; Conrod et al., 2001; King et al., 2002). Very few studies have systematically controlled these factors.
Our analysis found that visual and limbic brain regions were sensitive to the effects of alcohol. Emotional facial expressions activated higher order visual areas related to emotion-- including lingual and superior temporal gyri as well as the affective division of the anterior cingulate as has been previously reported in studies exploring the effects of emotional stimuli on brain activation (Devinsky et al., 1995; Phillips et al., 2003; Vuilleumier, 2005). This result is consistent with previous findings that recruitment of these regions is enhanced by emotionally-valenced visual stimuli (Vuilleumier, 2005). Importantly, the increased response to the fearful faces that we observed in the placebo condition was abolished in the alcohol condition. This suggests that alcohol may have attenuated the increased sensitivity of the visual system and limbic areas to emotionally threatening stimuli, and this may in part account for alcohol’s anxiolytic effect. An alternative explanation involves alcohol’s ability to increase activation in dopamine terminal regions, including amygdala, during the viewing of neutral faces. This increase in amygdala BOLD signal during neutral face presentation decreases the difference in amygdala activity between fearful and neutral faces, making the amygdala less able to act as a detector of threatening stimuli. This may not only lead to anxiolysis, but may also trigger an increase in both approach and aggression in some individuals.
The rewarding effects of alcohol in striatal brain areas
More than a third of the volume of the striatum was activated by alcohol across emotional conditions. The VS, particularly the NAcc, is critical in the reward system of the brain (Robinson and Berridge, 1993; Koob and Nestler, 1997; Everitt and Wolf, 2002), and lesions in this brain region decrease the rewarding effects of many drugs of abuse (Di Chiara, 2000). The reinforcing effects of alcohol most likely involve multiple neurotransmitter systems, including the dopaminergic, opioidergic, glutamatergic, GABAergic, and serotonergic systems. The increase in BOLD signal in the striatum may result from the increased firing rate of dopaminergic neurons secondary to the disinhibitory effect mediated through GABAergic interneurons and a decrease in glutamate-related potassium currents in the ventral tegmental area (Pierce and Kumaresan, 2006). A recent review of animal pharmacological MRI suggests that NAcc dopamine release increases local BOLD signal via postsynaptic D1 receptor activation (Knutson and Gibbs, 2007).
Consistent with previous studies that have shown significant inter-subject variability in subjective responses to alcohol at constant breath alcohol concentrations (Holdstock and de Wit, 1998, 2001), we did not find a correlation between subjective ratings of intoxication and actual BACs. We also did not find a correlation between BOLD response and actual BAC, which was not entirely unexpected given that the infusion method was designed to minimize the inter-subject variability in BAC exposure. We did find a significant association between BOLD response in the NAcc and subjective perceptions of intoxication, suggesting that under conditions where the BAC is held constant, the intensity of the subjective feeling of intoxication is associated with VS activation.
In addition, our results suggest that alcohol-mediated striatal activation can be modulated by negative emotional stimuli. The participants’ decreased striatal activation when viewing fearful faces suggests that the threatening stimuli may have attenuated the rewarding effects of the alcohol in the striatum, suggesting that context and environment influence the intensity of activation during intoxication.
Conclusions and future directions
This study demonstrates robust activation in response to intravenous alcohol infusion in the VS, an area that is critical in the acquisition and maintenance of addictive behavior. We were able to correlate striatal activation with subjective ratings of intoxication, indicating that the BOLD change in this area is directly related to an individual’s subjective experience of alcohol’s effects. Alcohol also modulates emotional processing in limbic and visual regions by decreasing the difference in activation between threatening and non-threatening stimuli, which may contribute to both the anxiolytic properties of alcohol, and to risky decision-making during intoxication. The data also indicate an interaction between alcohol and fearful emotional stimuli, such that fearful stimuli decrease striatal activation.
Although this study is underpowered to assess gender differences, future studies should examine whether alcohol has different effects on emotion in men and women, as previous research has shown that gender does influence emotional processing. For example, Klein and colleagues found no significant differences in activation could be found between pleasant and unpleasant stimuli in men, but significantly more activation to unpleasant than pleasant cues in women (Klein et al., 2003). Furthermore, studies can assess gender differences in mood, striatal alcohol response, and any possible interactions between the subject’s gender and the gender of the facial stimuli.
Future studies should also further explore the interaction between alcohol and emotion in alcohol-dependent patients and in individuals at risk for alcoholism. Previous studies have demonstrated differences between controls and alcohol-dependent patients (Heinz et al., 2007; Salloum et al., 2007), and between nonabusing adults with and without a family history of alcoholism (Glahn et al., 2007), in brain regions involved in the processing of emotional stimuli. None of these studies, however, has examined differences among these groups in the effects of acute alcohol administration. These studies could enhance our understanding of how the neural correlates of intoxication and emotion contribute to addiction and risky behavior while intoxicated. In addition, it is possible that attenuation of the alcohol-mediated striatal BOLD response could be used as a surrogate marker for the clinical effectiveness of medications being developed for the treatment of alcoholism.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the Division of Intramural Clinical and Biological Research of the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, part of the National Institutes of Health.
References
- Berns GS, McClure SM, Pagnoni G, Montague PR. Predictability modulates human brain response to reward. J Neurosci. 2001;21:2793–2798. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-08-02793.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjork JM, Knutson B, Fong GW, Caggiano DM, Bennett SM, Hommer DW. Incentive-elicited brain activation in adolescents: similarities and differences from young adults. J Neurosci. 2004;24:1793–1802. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4862-03.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard RJ, Magee L, Veniegas R, Blanchard DC. Alcohol and anxiety: ethopharmacological approaches. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1993;17:171–182. doi: 10.1016/0278-5846(93)90041-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blekher T, Ramchandani VA, Flury L, Foroud T, Kareken D, Yee RD, Li TK, O'Connor S. Saccadic eye movements are associated with a family history of alcoholism at baseline and after exposure to alcohol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2002;26:1568–1573. doi: 10.1097/01.ALC.0000033121.05006.EF. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boileau I, Assaad JM, Pihl RO, Benkelfat C, Leyton M, Diksic M, Tremblay RE, Dagher A. Alcohol promotes dopamine release in the human nucleus accumbens. Synapse. 2003;49:226–231. doi: 10.1002/syn.10226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breiter HC, Gollub RL, Weisskoff RM, Kennedy DN, Makris N, Berke JD, Goodman JM, Kantor HL, Gastfriend DR, Riorden JP, Mathew RT, Rosen BR, Hyman SE. Acute effects of cocaine on human brain activity and emotion. Neuron. 1997;19:591–611. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80374-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen MS. Parametric analysis of fMRI data using linear systems methods. Neuroimage. 1997;6:93–103. doi: 10.1006/nimg.1997.0278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrod PJ, Peterson JB, Pihl RO. Reliability and validity of alcohol-induced heart rate increase as a measure of sensitivity to the stimulant properties of alcohol. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2001;157:20–30. doi: 10.1007/s002130100741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coop CF, McNaughton N, Warnock K, Laverty R. Effects of ethanol and Ro 15–4513 in an electrophysiological model of anxiolytic action. Neuroscience. 1990;35:669–674. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90337-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin WR, Fromme K. Alcohol use and serial monogamy as risks for sexually transmitted diseases in young adults. Health Psychol. 2002;21:229–236. doi: 10.1037//0278-6133.21.3.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox RW. AFNI: software for analysis and visualization of functional magnetic resonance neuroimages. Comput Biomed Res. 1996;29:162–173. doi: 10.1006/cbmr.1996.0014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva GE, Vendruscolo LF, Takahashi RN. Effects of ethanol on locomotor and anxiety-like behaviors and the acquisition of ethanol intake in Lewis and spontaneously hypertensive rats. Life Sci. 2005;77:693–706. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2005.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wit H, McCracken SG. Ethanol self-administration in males with and without an alcoholic first-degree relative. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1990;14:63–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1990.tb00448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devinsky O, Morrell MJ, Vogt BA. Contributions of anterior cingulate cortex to behaviour. Brain. 1995;118(Pt 1):279–306. doi: 10.1093/brain/118.1.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Chiara G. Role of dopamine in the behavioural actions of nicotine related to addiction. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000;393:295–314. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(00)00122-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everitt BJ, Wolf ME. Psychomotor stimulant addiction: a neural systems perspective. J Neurosci. 2002;22:3312–3320. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-09-03312.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald DA, Angstadt M, Jelsone LM, Nathan PJ, Phan KL. Beyond threat: amygdala reactivity across multiple expressions of facial affect. Neuroimage. 2006;30:1441–1448. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giancola PR, Zeichner A. The biphasic effects of alcohol on human physical aggression. J Abnorm Psychol. 1997;106:598–607. doi: 10.1037//0021-843x.106.4.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giancola PR, Helton EL, Osborne AB, Terry MK, Fuss AM, Westerfield JA. The effects of alcohol and provocation on aggressive behavior in men and women. J Stud Alcohol. 2002;63:64–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glahn DC, Lovallo WR, Fox PT. Reduced amygdala activation in young adults at high risk of alcoholism: studies from the Oklahoma family health patterns project. Biol Psychiatry. 2007;61:1306–1309. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.09.041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinz A, Wrase J, Kahnt T, Beck A, Bromand Z, Grusser SM, Kienast T, Smolka MN, Flor H, Mann K. Brain activation elicited by affectively positive stimuli is associated with a lower risk of relapse in detoxified alcoholic subjects. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2007;31:1138–1147. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2007.00406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdstock L, de Wit H. Individual differences in the biphasic effects of ethanol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1998;22:1903–1911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdstock L, de Wit H. Individual differences in responses to ethanol and d-amphetamine: a within-subject study. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2001;25:540–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King AC, Houle T, de Wit H, Holdstock L, Schuster A. Biphasic alcohol response differs in heavy versus light drinkers. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2002;26:827–835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein S, Smolka MN, Wrase J, Grusser SM, Mann K, Braus DF, Heinz A. The influence of gender and emotional valence of visual cues on FMRI activation in humans. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2003;36 Suppl 3:S191–S194. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-45129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson B, Cooper JC. Functional magnetic resonance imaging of reward prediction. Curr Opin Neurol. 2005;18:411–417. doi: 10.1097/01.wco.0000173463.24758.f6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson B, Gibbs SE. Linking nucleus accumbens dopamine and blood oxygenation. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2007;191:813–822. doi: 10.1007/s00213-006-0686-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson B, Adams CM, Fong GW, Hommer D. Anticipation of increasing monetary reward selectively recruits nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci. 2001;21:RC159. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-16-j0002.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koob GF. Drugs of abuse: anatomy, pharmacology and function of reward pathways. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992;13:177–184. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90060-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koob GF, Nestler EJ. The neurobiology of drug addiction. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1997;9:482–497. doi: 10.1176/jnp.9.3.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koob GF, Roberts AJ, Schulteis G, Parsons LH, Heyser CJ, Hyytia P, Merlo-Pich E, Weiss F. Neurocircuitry targets in ethanol reward and dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1998;22:3–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwo PY, Ramchandani VA, O'Connor S, Amann D, Carr LG, Sandrasegaran K, Kopecky KK, Li TK. Gender differences in alcohol metabolism: relationship to liver volume and effect of adjusting for body mass. Gastroenterology. 1998;115:1552–1557. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(98)70035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeDoux J. The emotional brain, fear, and the amygdala. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2003;23:727–738. doi: 10.1023/A:1025048802629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levenson RW, Sher KJ, Grossman LM, Newman J, Newlin DB. Alcohol and stress response dampening: pharmacological effects, expectancy, and tension reduction. J Abnorm Psychol. 1980;89:528–538. doi: 10.1037//0021-843x.89.4.528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukas SE, Mendelson JH, Benedikt RA, Jones B. EEG, physiologic and behavioral effects of ethanol administration. NIDA Res Monogr. 1986;67:209–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin CS, Earleywine M, Musty RE, Perrine MW, Swift RM. Development and validation of the Biphasic Alcohol Effects Scale. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1993;17:140–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1993.tb00739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto DEP. Japanese and Caucasian Facial Expressions of Emotion and Neutral Faces. San Francisco, CA: San Francisco State University; 1988. [Google Scholar]
- McClure SM, Daw ND, Montague PR. A computational substrate for incentive salience. Trends Neurosci. 2003;26:423–428. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(03)00177-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mokdad AH, Marks JS, Stroup DF, Gerberding JL. Actual causes of death in the United States, 2000. Jama. 2004;291:1238–1245. doi: 10.1001/jama.291.10.1238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morzorati SL, Ramchandani VA, Flury L, Li TK, O'Connor S. Self-reported subjective perception of intoxication reflects family history of alcoholism when breath alcohol levels are constant. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2002;26:1299–1306. doi: 10.1097/01.ALC.0000025886.41927.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor S, Ramchandani VA, Li TK. PBPK modeling as a basis for achieving a steady BrAC of 60 +/− 5 mg% within ten minutes. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2000;24:426–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Doherty JP, Deichmann R, Critchley HD, Dolan RJ. Neural responses during anticipation of a primary taste reward. Neuron. 2002;33:815–826. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(02)00603-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagnoni G, Zink CF, Montague PR, Berns GS. Activity in human ventral striatum locked to errors of reward prediction. Nat Neurosci. 2002;5:97–98. doi: 10.1038/nn802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips ML, Drevets WC, Rauch SL, Lane R. Neurobiology of emotion perception I: The neural basis of normal emotion perception. Biol Psychiatry. 2003;54:504–514. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(03)00168-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce RC, Kumaresan V. The mesolimbic dopamine system: the final common pathway for the reinforcing effect of drugs of abuse? Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2006;30:215–238. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2005.04.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramchandani VA, Kwo PY, Li TK. Effect of food and food composition on alcohol elimination rates in healthy men and women. J Clin Pharmacol. 2001;41:1345–1350. doi: 10.1177/00912700122012814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramchandani VA, Bolane J, Li TK, O'Connor S. A physiologically-based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model for alcohol facilitates rapid BrAC clamping. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1999;23:617–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramchandani VA, Flury L, Morzorati SL, Kareken D, Blekher T, Foroud T, Li TK, O'Connor S. Recent drinking history: association with family history of alcoholism and the acute response to alcohol during a 60 mg% clamp. J Stud Alcohol. 2002;63:734–744. doi: 10.15288/jsa.2002.63.734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson TE, Berridge KC. The neural basis of drug craving: an incentive-sensitization theory of addiction. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1993;18:247–291. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(93)90013-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salloum JB, Ramchandani VA, Bodurka J, Rawlings R, Momenan R, George D, Hommer DW. Blunted rostral anterior cingulate response during a simplified decoding task of negative emotional facial expressions in alcoholic patients. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2007;31:1490–1504. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2007.00447.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreckenberger M, Amberg R, Scheurich A, Lochmann M, Tichy W, Klega A, Siessmeier T, Grunder G, Buchholz HG, Landvogt C, Stauss J, Mann K, Bartenstein P, Urban R. Acute alcohol effects on neuronal and attentional processing: striatal reward system and inhibitory sensory interactions under acute ethanol challenge. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004;29:1527–1537. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spanagel R, Montkowski A, Allingham K, Stohr T, Shoaib M, Holsboer F, Landgraf R. Anxiety: a potential predictor of vulnerability to the initiation of ethanol self-administration in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1995;122:369–373. doi: 10.1007/BF02246268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein EA, Pankiewicz J, Harsch HH, Cho JK, Fuller SA, Hoffmann RG, Hawkins M, Rao SM, Bandettini PA, Bloom AS. Nicotine-induced limbic cortical activation in the human brain: a functional MRI study. Am J Psychiatry. 1998;155:1009–1015. doi: 10.1176/ajp.155.8.1009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talairach J, Tournoux P. Co-Planar Stereotaxic Atlas of the Human Brain. New York: Thieme; 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Turkkan JS, Stitzer ML, McCaul ME. Psychophysiological effects of oral ethanol in alcoholics and social drinkers. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1988;12:30–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1988.tb00129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuilleumier P. How brains beware: neural mechanisms of emotional attention. Trends Cogn Sci. 2005;9:585–594. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2005.10.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang GJ, Volkow ND, Franceschi D, Fowler JS, Thanos PK, Scherbaum N, Pappas N, Wong CT, Hitzemann RJ, Felder CA. Regional brain metabolism during alcohol intoxication. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2000;24:822–829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D, Clark LA, Tellegen A. Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: the PANAS scales. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1988;54:1063–1070. doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.54.6.1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]