Figure 2.
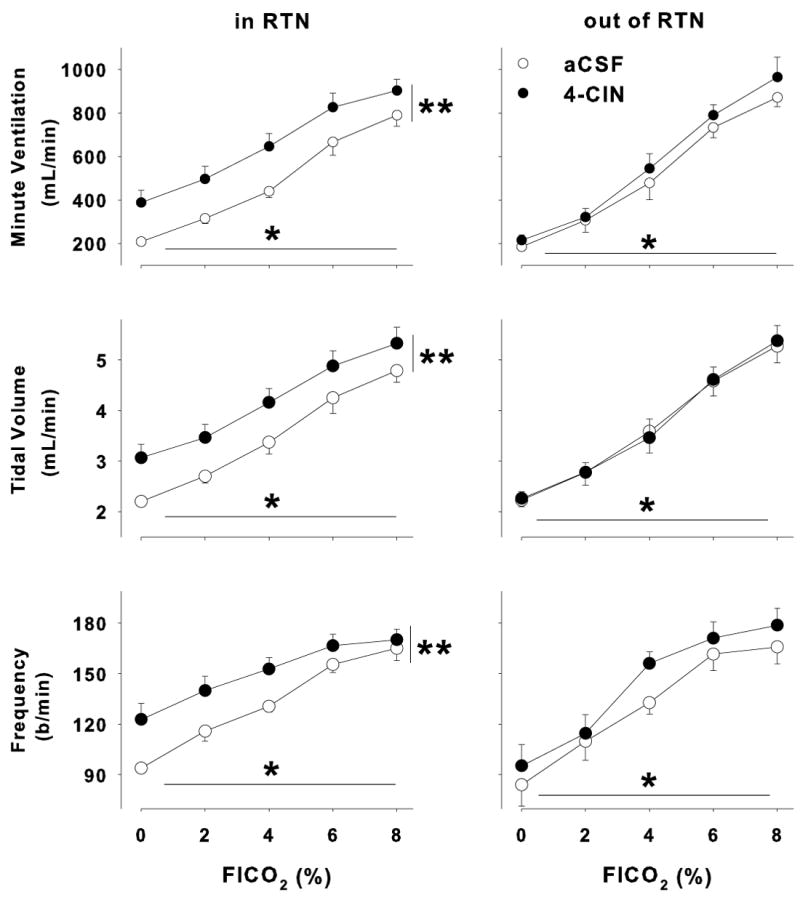
Ventilatory effects of 4-CIN perfusion unilaterally in the RTN. (A) Minute ventilation, (B) tidal volume and (C) frequency increased significantly as the fractional inspired CO2 increased (P <0.01 for all three variables). In addition, focal unilateral perfusion of 4-CIN into the RTN increased minute ventilation, tidal volume and frequency at all levels of FICO2 (P < 0.01 for all three variables; left panels; n = 9). On the other hand, 4-CIN perfused focally in the ventral medulla outside the area of the RTN did not change minute ventilation, tidal volume or frequency (n = 3), although increasing the FICO2 increased these variables just as it had in the RTN treatment group.
