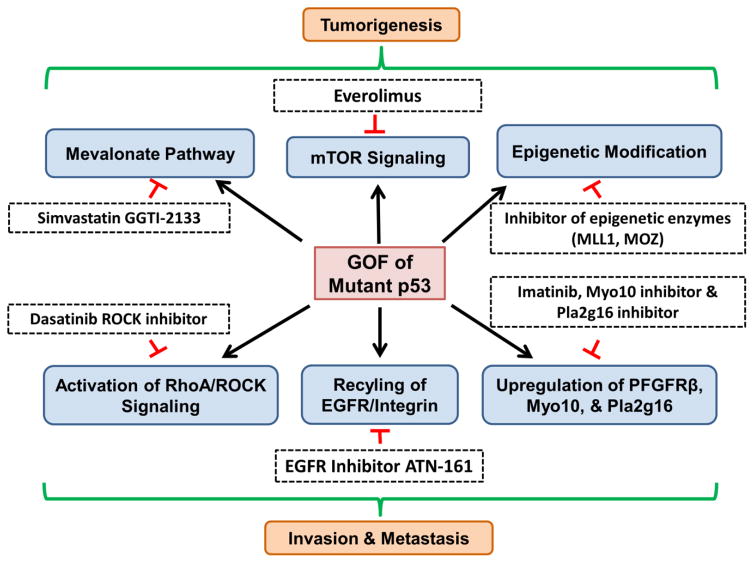
Figure 2. Strategies to target pathways induced by p53 GOF mutants.
Mutant p53 gains new functions to promote tumorigenesis by activation of the metabolic melanovate pathway or upregulation of epigenetic enzymes. Drugs that target the melanovate pathway (simvastatin, GGTI-2133) or epigenetic enzymes (MLL1, MOZ inhibitors) show promise for the treatment of p53 mutant cancers. Cytoplasmic mutant p53 also promote tumor growth through activation of mTOR signaling, providing an opportunity to using mTOR inhibitors to treat cancers with cytoplasmic mutant p53. In addition, mutant p53 often gains novel function(s) to promote tumor invasion and metastasis through activation of cell invasion pathways (PDGFRβ signaling, RhoA/ROCK, EGFR/integrin recycling, Myo10, Pla2g16). Small molecular inhibitors (ROCK inhibitor, EGFR inhibitor, Myo10 inhibitor and Pla2g16 inhibitor) have been used to target each pathway to inhibit the metastatic ability of p53 mutant cancers.