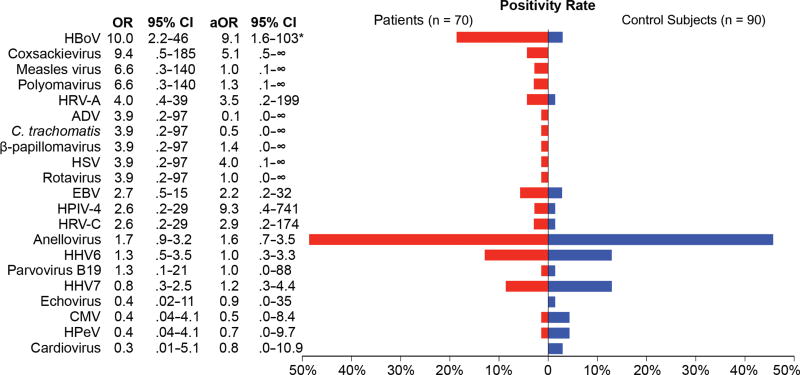
Figure 2.
Viruses detected by RNA sequencing and/or pan-viral group polymerase chain reaction in children with pneumonia with no identifiable etiology (n = 70; red) and asymptomatic control subjects (n = 90; blue). A total of 20 different human viruses were detected in nasopharyngeal/oropharyngeal samples. In addition, Chlamydia trachomatis was detected in 1 newborn child with pneumonia. Fifteen viruses were more frequently detected in patients than control subjects (odds ratios >1), with human bocavirus (P < .001) having significant associations with community-acquired pneumonia. Abbreviations: ADV, adenovirus; aOR, adjusted odds ratio (adjusted for season and age group); C. trachomatis, Chlamydia trachomatis; CI, confidence interval; CMV, cytomegalovirus; HBoV, human bocavirus; HHV6, human herpesvirus 6; HHV7, human herpesvirus 7; HPeV, human parechovirus; HPIV-4, human parainfluenza virus type 4; HRV-A, human rhinovirus A; HRV-C, human rhinovirus C; HSV, herpes simplex virus; OR, odds ratio.