Table 1.
Signaling differences and mutations in tumors that have either mutant p53 or loss of p16ink4a
| Mutant p53 | Loss of pl6 |
|---|---|
| p42/44 MAPK possible tumor suppressor | p42/44 MAPK pro-tumorigenic |
| Negative for Wilms' Tumor 1 | Positive for Wilms' Tumor 1 |
| Ameboid morphology | Mesenchymal morphology |
| Lymph nodes | Hematogeneus |
| Radiation sensitive | Radiation resistant |
| Notch inactivate | Notch activation |
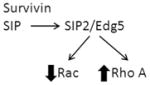
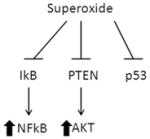
| Survivin | Superoxide |
|
|
| Stat 3 | Stat 3/5 |
| Hif1α | Hif2α |
| Extracellular membrane deposition | |
| Increased telomerase |
These represent polar opposites, but in some very advanced tumors, there may be both mutant p53 and loss of p16ink4a, leading to potential signaling plasticity
