Fig. 3.
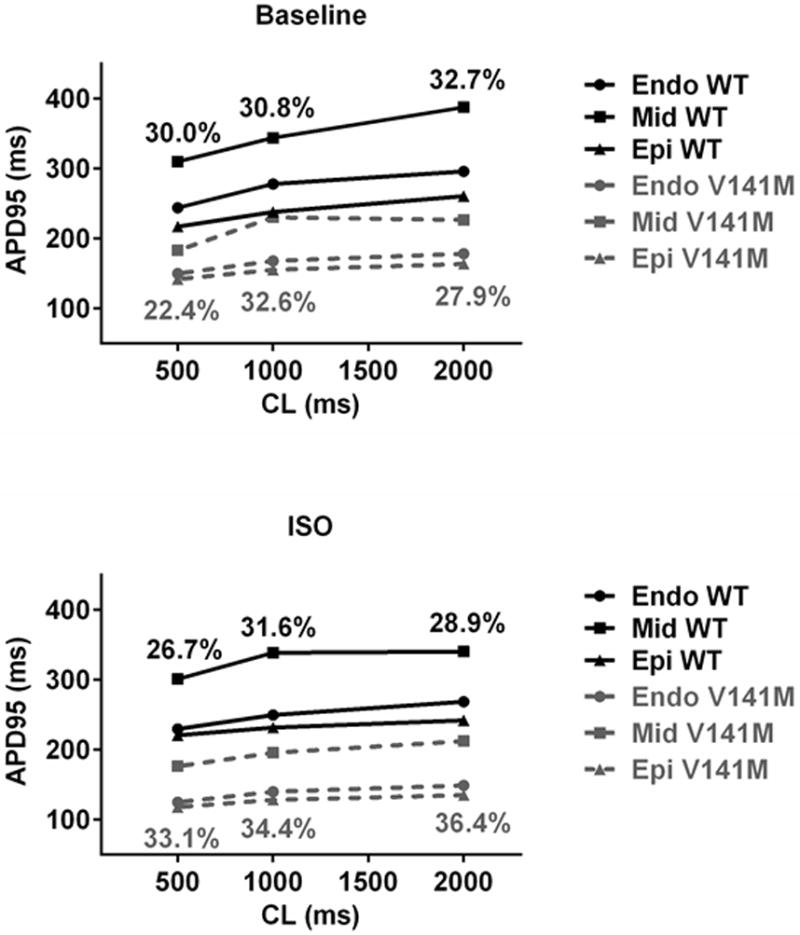
AP simulations show blunted APD rate adaptation and increased transmural heterogeneity of APD associated with the V141M KCNQ1 mutation. At fast cycle lengths of 500 ms and slow cycle lengths of 2000 ms, WT KCNQ1 APD increased 52.0, 77.6, and 43.5 ms in Endo, Mid and Epi, respectively, but V141M KCNQ1 mutation APD increased 28.3, 43.7, and 21.5 ms respectively (upper panel). At cycle lengths of 500 and 2000 ms, APD heterogeneity diminished from 30.0 to 26.7% and from 32.7 to 28.9% respectively in the presence of isoproterenol (ISO) challenge in WT. In contrast, the heterogeneity of APD was augmented with ISO in V141M KCNQ1. In the presence of ISO, APD heterogeneity increased from 22.4 to 33.1%, from 27.9 to 36.4%, and from 32.6 to 34.4%, at cycle lengths of 500, 2000, or 1000 ms, respectively. The heterogeneity increase was due to preferential abbreviation of epicardial (Epi) and endocardial (Endo) cells as compared with mid-myocardial (Mid) cells
