Figure 3.
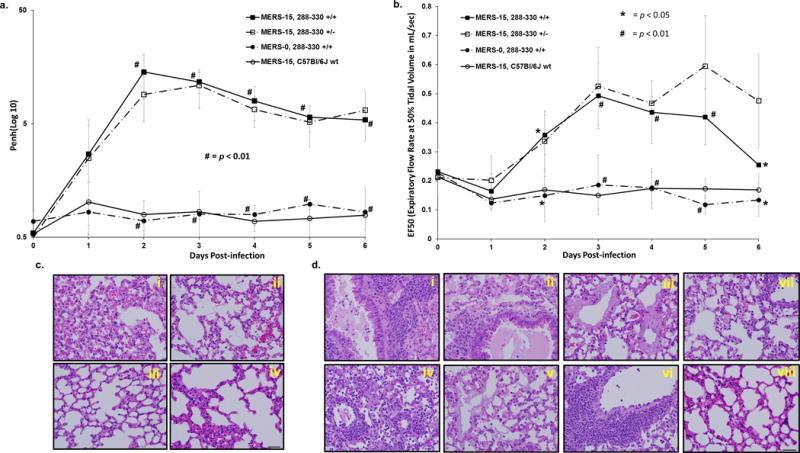
Lung function in MERS-15-infected mice. Respiratory function was monitored in live mice through day 6 p.i. using whole-body plethysmography to measure enhanced pause (Penh) (a) and the expiratory flow rate at 50% tidal volume (EF50) (b) in 288-330+/+ + MERS-15 (n = 9); 288-330+/− + MERS-15 (n = 4), 288-330+/+ + MERS-0 (n = 3), and C57Bl/6J wt + MERS-15 (n = 3). Data are daily averages ±SD. Student t-test was used to compare 288-330+/+ mice infected with MERS-15 and MERS-0, # is p < 0.01 and * is p < 0.05. (c) Pathology of lungs from infected mice at day 3 p.i. demonstrate severe inflammation for 288-330+/+ (i) and 288-330+/− (ii) infected with MERS-15, and moderate inflammation for 288-330+/+ + MERS-0 (iii) and C57Bl/6J wt + MERS-15 (iv). (d) Pathology at day 6 post-infection for 288-330+/+ + MERS-15 images demonstrate severe inflammation and edema in large airways and alveoli (i) and (ii), and hyaline membrane formation (iii). 288-330+/− + MERS-15 exhibit severe inflammation throughout parenchyma (iv), hyaline membrane formation (v), and perivascular cuffing (vi). 288-330+/+ + MERS-0 (vii) or C57Bl/6Jwt + MERS-15 (viii) exhibit mild-to-moderate inflammation. All images are at 40X magnification. H&E images are representative of at least 3 samples. Scale bars in lower right panels are 1mm.
