Figure 3.
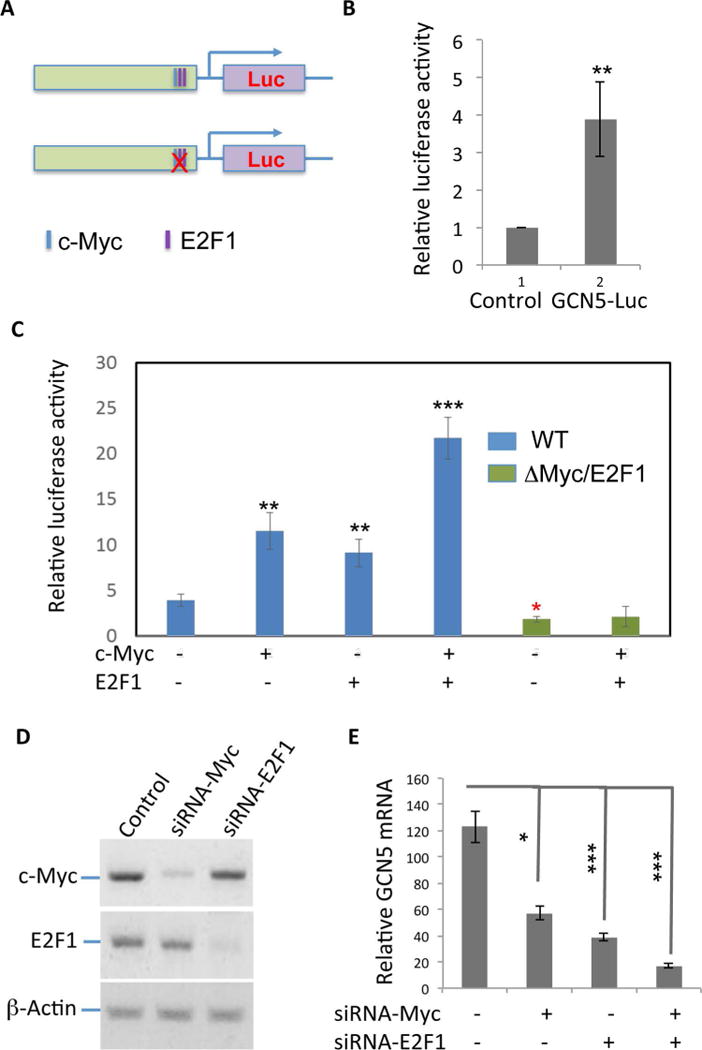
The transcription factors c-Myc is involved in GCN5 mRNA transcription. (A) GCN5 promoter region was amplified by PCR using genomic DNA from PC12 cells as template. The amplified DNA fragment was subcloned into a luciferase reporter vector. Point mutations of the c-Myc and E2F1 binding sites are indicated. (B) GCN5 luciferase or control luciferase plasmid DNA was transfected into HCT116 human colon cancer cells. Forty-eight hours after transfection, the luciferase was determined, and the relative fold changes are shown. (C) GCN5 luciferase plasmid or its mutant was transfected with c-Myc or E2F1 expression plasmids or both. The luciferase activity was determined as in (B). (D, E) c-Myc-specific siRNAs were transfected into HCT116 cells. The protein expression levels of c-Myc (top) were determined by Western blotting using β-actin as a loading control (bottom) (D). The expression levels of GCN5 mRNA in the knockdown cells were analyzed by real-time PCR (E). Student’s t-test was used for the statistical analysis. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001.
