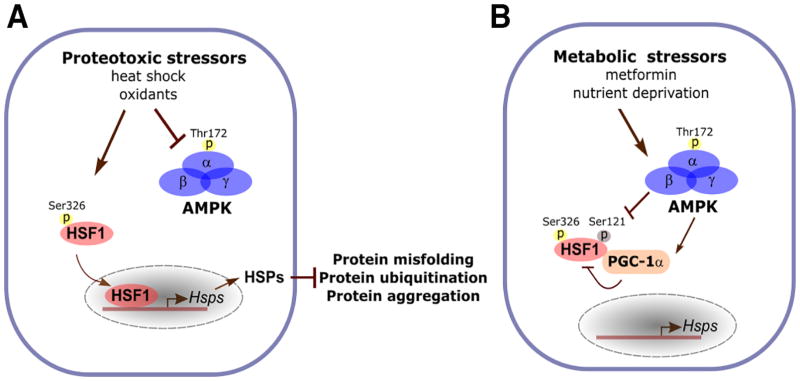
Figure 1. Suppression of the HSF1-mediated PSR by metabolic stressors.
A: Proteotoxic stressors activate HSF1 and its mediated PSR. Under proteotoxic stress, Ser326 phosphorylation is a key post-translational modification activating HSF1. In addition, heat stress also inactivates AMPK and blocks its mediated Ser121 phosphorylation, a modification inhibitory to HSF1 activation. Under proteotoxic stress, induced HSP expression through the PSR plays a critical role in preserving cellular proteostasis and enhance survival. B: In contrast to proteotoxic stressors, metabolic stressors, including metformin and nutrient deprivation, suppresses HSF1 activation through AMPK activation. Activated AMPK phosphorylates HSF1 directly at Ser121 to impair the nuclear translocation and DNA binding of HSF1. In addition, AMPK can suppress the transcriptional activity of HSF1 indirectly through PGC-1α. Upon phosphorylated and activated by AMPK, PGC-1α acts as a transcriptional repressor by physically interacting with HSF1. Though suppression of the PSR, metabolic stressors exacerbate the disruption of proteostasis by proteotoxic stressors.