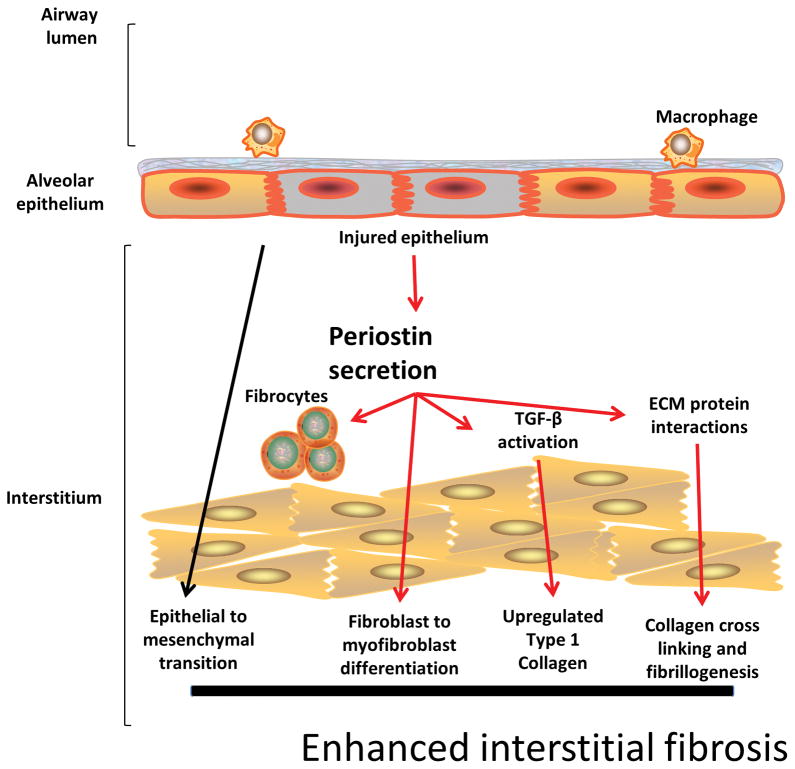
Figure 2. Contributions of Periostin to IPF pathophysiology.
In IPF, recurrent idiopathic epithelial cell injury results in inflammation. Periostin is highly expressed in the lungs and subsequently leads to TGF-B activation, increased type 1 collagen production, promotes fiber cross linking and enhanced stiffening of the interstitial matrix. Periostin mediates fibroblast to myofibroblast differentiation and studies from animal models support a role for periostin in epithelial to mesenchymal cell transition.