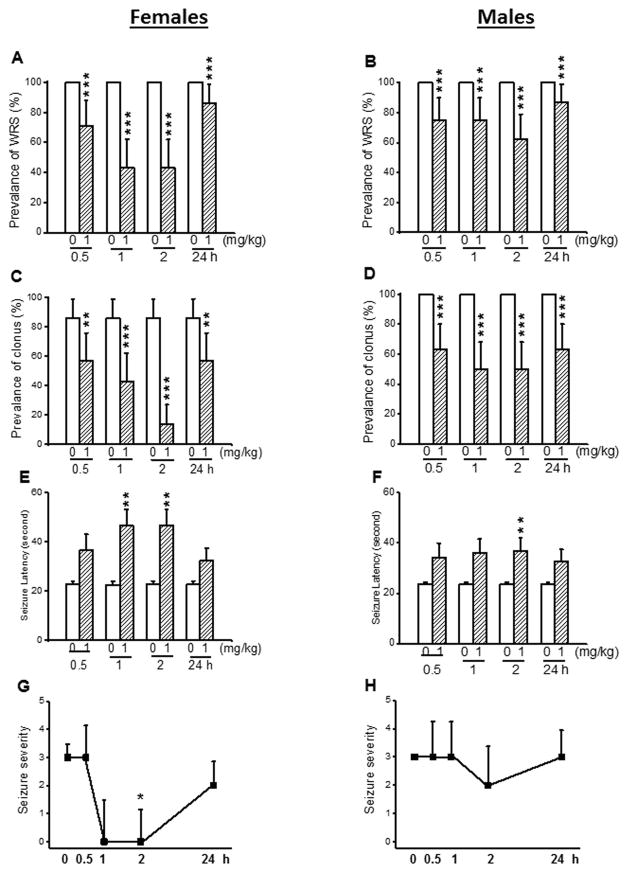
Figure 1.
Effects of acute capsazepine (CPZ) treatment at a dose of 1 mg/kg on occurrence of acoustically evoked seizures in female and male GEPR-3s. The anticonvulsant effects of CPZ were evaluated at different posttreatment time points of 0.5, 1, 2, and 24 hours. CPZ at a dose of 1 mg/kg (i.p.) markedly reduced the incidence of WRS in both female (n=7, panel A) and male (n=8, panel B) GEPR-3s. CPZ also reduced the prevalence of clonus in both female (panel C) and male (panel D) GEPR-3s. CPZ also delayed the onset of seizure in either female (panel E) or male (panel F) GEPR-3s. Time course of the effects of CPZ showed a transient, but complete seizure suppression by the 1st hour post-treatment in female GEPR-3s (panel G), while no anticonvulsant effect was observed in male GEPR-3s (panel H). For the prevalence of WRS and clonus, data represent the percentage (%)±standard error of proportion, and McNemar’s test was used for statistical analysis. For latency, data represent mean±S.E.M., and paired t-test was used for analysis. For seizure severity, data represent the median score±median average deviation, and Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used for statistical analysis. Opened and filled bar graphs represent controls (pre-CPZ) and CPZ treated GEPR-3s, respectively. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.