Figure 4.
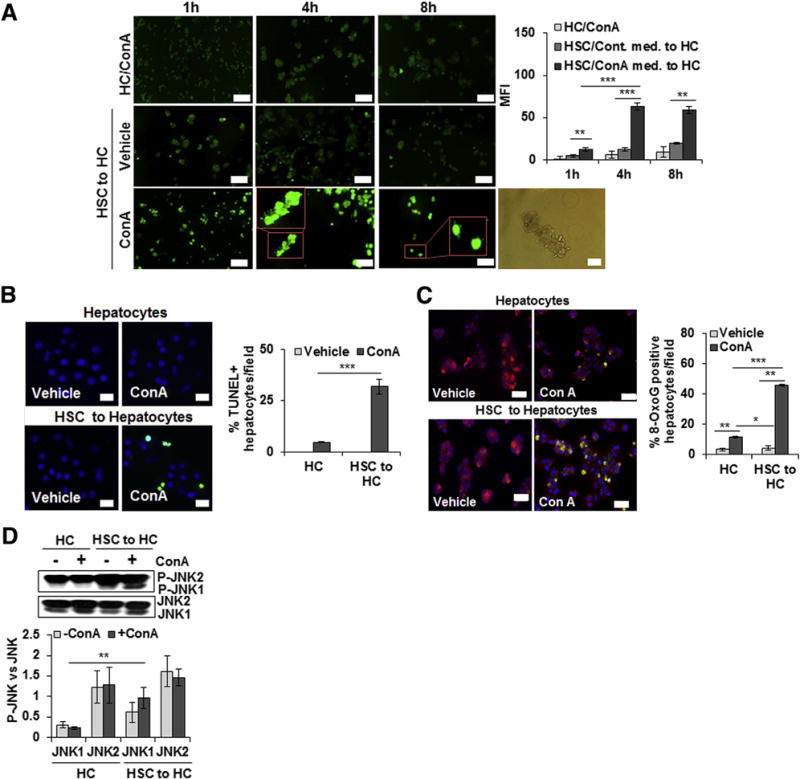
ConA-stimulated HSCs induce oxidative stress, apoptosis, and DNA damage in hepatocytes. A: Hepatocytes (HCs) or HSCs were incubated in medium containing 50 μg/mL ConA for 1, 4, or 8 hours (h). ConA-conditioned HSC medium was then transferred to hepatocytes. After 12 hours, generation of reactive oxygen species in hepatocytes was determined by 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin diacetate—based staining. Insets in bottom panels of A are high magnification of indicated areas. Phase-contrast image shows bleb formation in hepatocytes treated with ConA/HSC. B: Hepatocytes were incubated in medium containing 50 μg/mL ConA or medium conditioned by HSCs for 8 hours in absence or presence of ConA. After 12 hours, cells were washed and fixed, and TUNEL staining was performed. C: Hepatocytes were incubated in culture medium containing 15 μmol/L MitoTracker for 30 minutes, and immunostained with anti-oxioguanine 8 (8-OxoG) Ab (1:400) to detect DNA damage. DAPI was used for nuclear staining. D: Western blot shows phosphorylation of JNK (P-JNK) in hepatocytes, and the bar graph shows activation as quantified via densitometry. All images are representative of three separate experiments. Bar graphs show combined values from three independent experiments. Data are expressed as means ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. Scale bars: 100 mm (A, left panels, 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin diacetate—based staining at 1, 4, and 8 hours); 50 μm (A, right panel, phase-contrast image, B, and C). Original magnification, × 20 (A, insets). MFI, mean fluorescence intensity.
