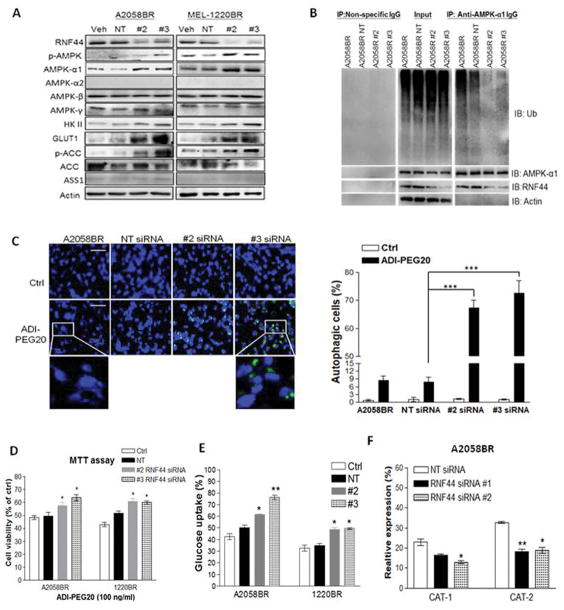
Fig. 3.
Silencing RNF44 in BR cells abrogates AMPK-α1 degradation, switches metabolism to glucose addiction, and restores autophagosome formation upon arginine deprivation. BR cells were transfected with individual siRNAs against RNF44, non-targeting (NT) siRNA (50 nM) or with transfection reagent alone (Veh, as a control group). Total cell lysates of these transfectants were subjected to immunoblotting (A) and immunoprecipitation of AMPK-α1 (B). (C) A2058BR cells were transfected with RNF44 siRNAs and treated with ADI-PEG20. Their autophagosomes and nuclei were separately stained with Cyto-ID (green) and Hoechst33342 (blue), and then visualized using fluorescent microscope (scale bar = 50 μm). Autophagy-positive cells were quantitated and presented as a bar graph. (D) Cell viability of these transfectants was analyzed by MTT after treatment with ADI-PEG20 (100 ng/ml) or completed medium for 48–72hr. (E) Glucose uptake was analyzed by 2-NBDG uptake with FACS. (F) CAT-1 and CAT-2 expressions were assessed by FACS and data were shown in a bar graph (n = 3, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.005).