Fig. 9.
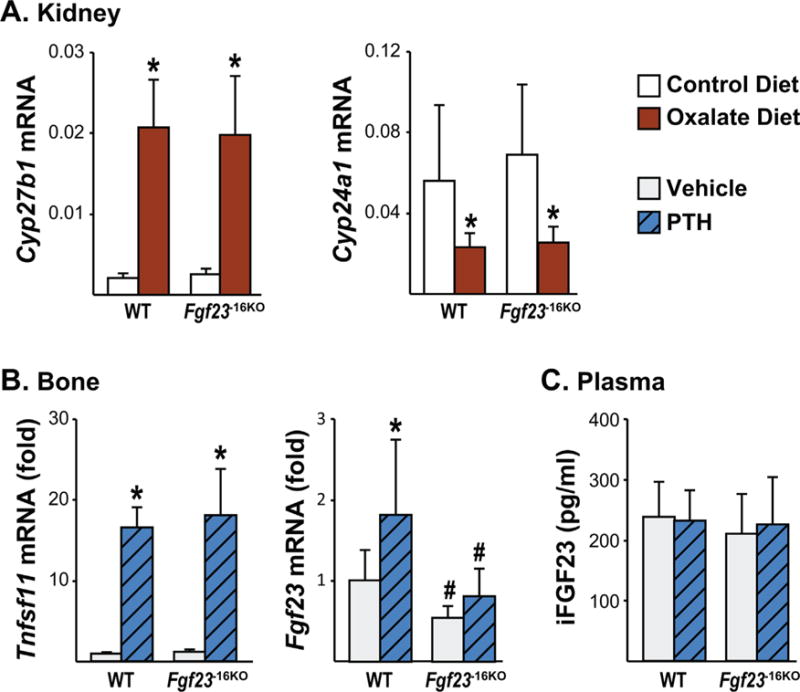
The −16kb enhancer of Fgf23 mediates the PTH-induced increase in Fgf23 transcription. (A) Eight-week-old male Fgf23−16KO mice and their wild-type (WT) littermates were fed control or oxalate diet for 1 week. Kidney Cyp27b1 and Cyp24a1 mRNA levels were measured by RT-PCR. Bars represent the mean ± SD of 5 to 7 mice/group. (B, C) Eight-week-old wild-type (WT) and Fgf23−16KO male mice were injected ip with 230 ng/g bw of PTH. Tissues were collected 1 hour after injection. (B) Tnfsf11 (RANKL) and Fgf23 mRNA levels were measured by RT-PCR. Bars represent the mean ± SD of 8 to 9 mice/group as fold by comparison to mean of WT vehicle group. (C) Circulating intact FGF23 (iFGF23) levels were measured 1 hour after PTH injection. Bars represent the mean ± SD of 8 to 9 mice/group. All statistical analysis between the groups were performed using two-way ANOVA with multiple comparison test using the Benjamini-Hochberg procedure and “a”, p < 0.05 magnitude of the difference (vehicle-PTH injection) is less in Fgf23−16KO mice compared with WT mice. *p < 0.05 effect of treatment within the same genotype; #p < 0.05 effect of genotype within same treatment.
